Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):25-32
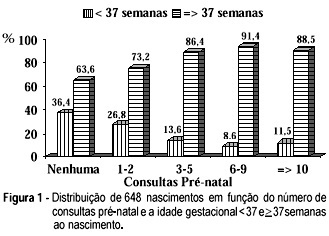
It is universally accepted that prenatal care has a beneficial impact on perinatal outcome. However, it is unclear whether access to early and frequent prenatal care influences the impact of pregnancy complications on birth weight. The objective of the present study was to determine the effectiveness of prenatal care, concerning antenatal visits (number and time of the first one), on gestational age and fetal weight at birth. We assessed prospectively the effect of the antenatal care in a group of 648 infants born consecutively at the University Hospital of Santa Maria, weighing from <1000 to >4000 g, and from <28 to >40 weeks of gestational age. Preterm delivery (<37 weeks) accounted for 17.7% of all deliveries, low birth-weight infants (<2500 g) for 20.5%, and very low birth-weight infants (<1000 g) for 2.8%. When the first antenatal visit was performed before the 12th week, only 5.1% of the babies were born with <37 weeks of gestational age or weight at birth of <2500 g. However, when the first visit was after the 28th week, the percentage of preterm delivery was 41.3% and of birth weight <2500 g was 43.5%. A significant association between higher frequency of antenatal visits, early care and decrease in preterm delivery frequency and low birth-weight infants was noted (p <0.001). We conclude that increase in the number of antenatal visits and early care can reduce the preterm delivery and low-birth weight infant rates.
Search
Search in:


Comments