Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo35
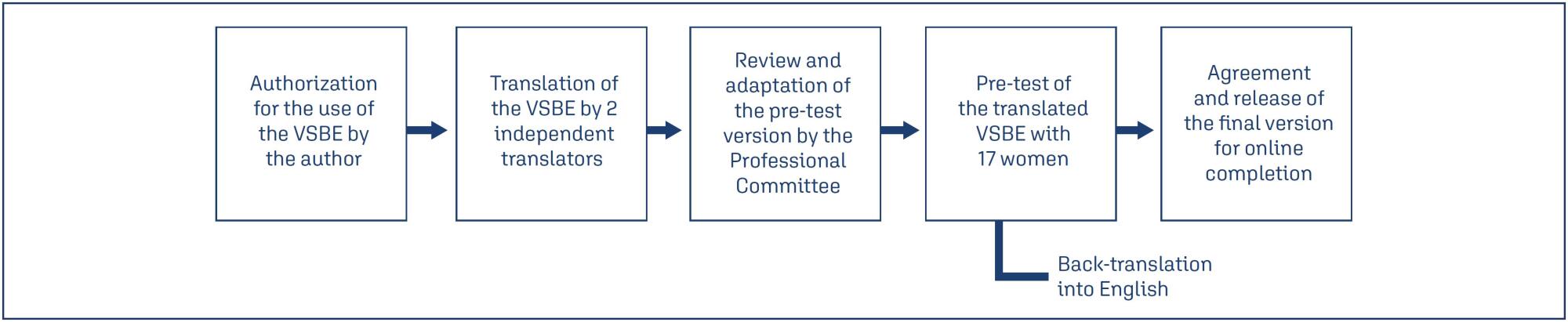
We aimed to translate and determine cultural validity of the Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale (VSBE) for Brazilian Portuguese language in postpartum women who underwent vaginal delivery with or without perineal laceration and cesarean section.
A cross-sectional study conducted virtually, with online data collection through a survey with 234 postpartum women of 975 that were invited. Clinical, sociodemographic, and psychometric variables from the VSBE questionnaire were analyzed (content validity index, internal consistency, test-retest reliability, construct/structural and discriminant validity). Multivariate analysis was performed to explore associated factors with the presence of perineal laceration.
One-hundred fifty-eight women experienced vaginal delivery, of which 24.79% had an intact perineum, 33.33% had perineal laceration, and 9.4% underwent episiotomy; and 76 participants had cesarean sections. Women with perineal laceration were older, presented dyspareunia and previous surgeries than women without perineal laceration (p<0.05). For VSBE, a high internal consistency (Cronbach's α > 0.7) was observed, but it did not correlate with Body Attractiveness Questionnaire and Female Sexual Function Index; however, it correlated with the presence of women sutured for perineal laceration. Moreover, VSBE presented good structural validity with two loading factors after exploratory factor analysis. VSBE also demonstrated discriminant validity between the presence or absence of perineal laceration. The presence of urinary incontinence (UI) (OR=2.716[1.015-4.667];p=0.046) and a higher VSBE total score (OR=1.056[1.037-1.075];p<0.001) were the only factors associated with perineal laceration.
Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale demonstrated appropriate translation and good internal consistency, discriminant/construct validity and reliability. Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale total score and presence of UI were associated with women that underwent perineal laceration.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):089-095
We evaluated internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and criterion validity of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) for postpartum women.
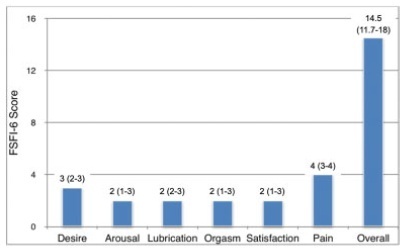
Therefore, questionnaires were applied to 100 sexually active women in the postpartum period. The Cronbach α coefficient was used to evaluate the internal consistency. Test-retest reliability was analyzed by Kappa for each item of the questionnaire and by the Wilcoxon parametric test, comparing the total scores of each evaluation. For the assessment of criterion validity, the FSFI was used as the gold standard and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). It was found that the internal consistency of the FSFI-6 questionnaire was considerably high (0.839).
The test-retest reliability results were satisfactory. It can also be stated that the FSFI-6 questionnaire presented excellent discriminant validity (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.926). Women may be considered as having sexual dysfunction if the overall FSFI-6 score is < 21, with 85.5% sensitivity, 82.2% specificity, positive likelihood ratio of 4.81 and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18.
We conclude that the Brazilian Portuguese version of FSFI-6 is valid for use in postpartum women.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):962-971
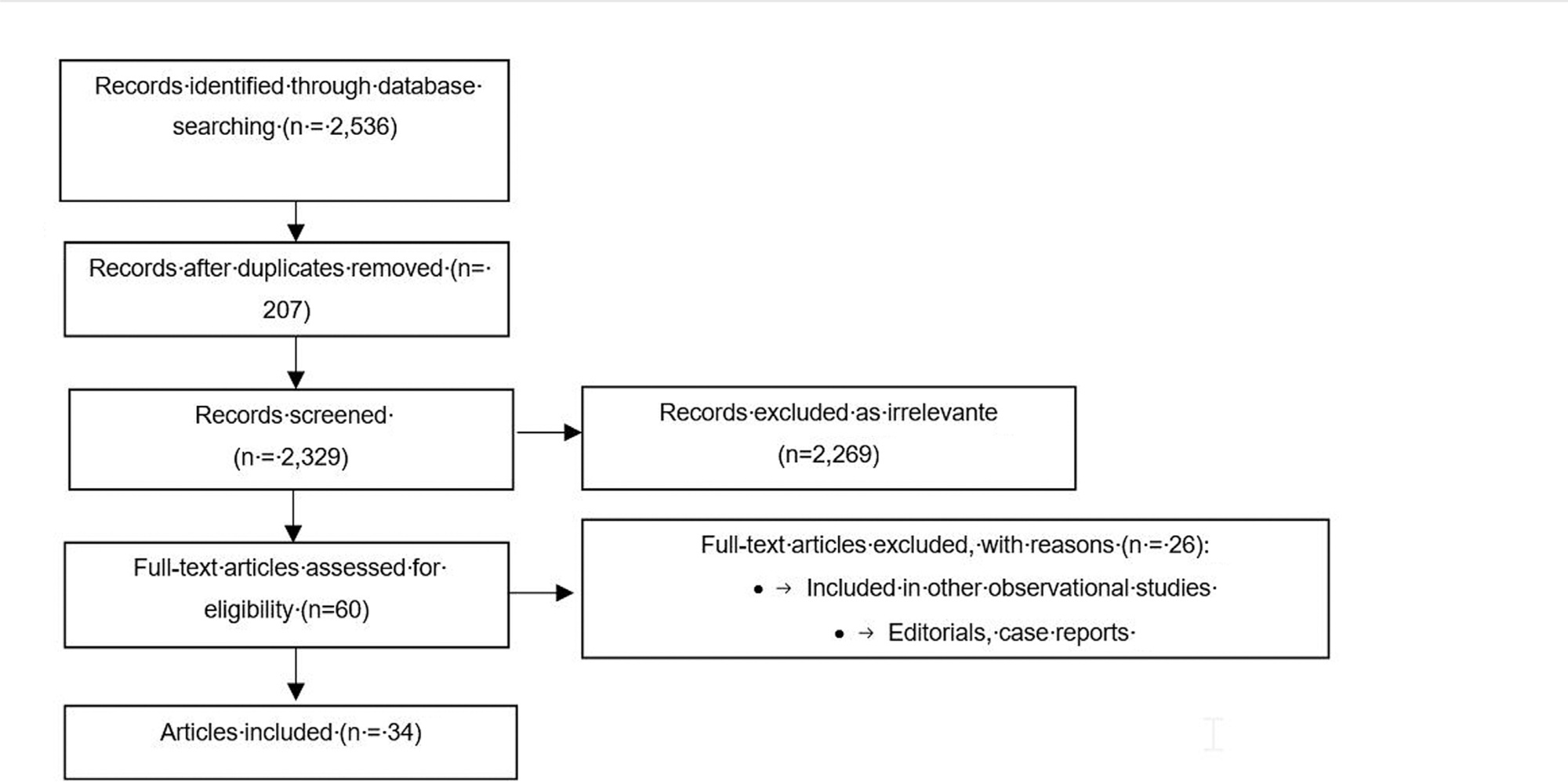
To explore the main sexuality complaints of gynecologic cancer survivors after treatment and to identify the care strategies provided.
Searches were conducted in six electronic databases: Scopus, Web of Science, LILACS, MEDLINE, PsychINFO, and EMBASE.
Articles published between 2010 and 2020 were selected and the following descriptors were used in the English language: female genital neoplasms and gynaecological cancer. The methodological quality of the studies used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT).
The primary data extracted were: names of the authors, year of publication, country of origin, objective and type of study, data collection instrument, sample size and age range, types of cancer, and symptoms affected with the strategies adopted.
A total of 34 out of 2,536 screened articles were included. The main strategies found for patient care were patient-clinician communication, practices for sexuality care, individualized care plan, multiprofessional team support, and development of rehabilitation programs. For sexuality care, the most common practices are pelvic physiotherapy sessions and the use of vaginal gels and moisturizers.
The main complaints identified in the scientific literature were low libido and lack of interest in sexual activity, vaginal dryness, pain during sexual intercourse, and stenosis. Different care strategies may be adopted, such as follow-up with a multidisciplinary health team and sexual health rehabilitation programs, which could minimize these symptoms and ensure the quality of life of patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):522-529
To assess the sexual function and associated factors in postmenopausal women.
This a descriptive, cross-sectional study with 380 women aged 40 to 65 years, users of public health services in 2019. Questionnaires were applied on demographic characteristics, on climacteric symptoms (menopause rating scale) and on sexual function (sexual quotient, female version). Bivariate andmultiple analyses by logistic regression were performed, with adjusted odds ratios (ORad) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs).
More than half (243/64%) of the participating women were at risk of sexual dysfunction, with lower scores in the domains of sexual desire and interest, comfort, orgasm, and satisfaction. Women with a partner (ORad 2.07; 95%CI 1.03-4.17) and those who reported sleep problems (ORad 2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.19), depressed mood (ORad 2.03; 95%CI 1.32-3.10), sexual complaints (ORad 8.16; 95%CI 5.06-13.15), and vaginal dryness (ORad 3.44; 95%CI 2.22-5.32) showed greater chance of sexual dysfunction.
There was a high prevalence of sexual dysfunction, with the influence of conjugality and climacteric symptoms on sexual function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):467-473
To assess the sexual function of women with spina bifida (SB), and to verify the factors that influence their sexual function.
A cross-sectional study in which a validated female-specific questionnaire was applied to 140 SB female patients from four different cities (Porto Alegre, Brazil; and Barcelona, Madrid, and Málaga, Spain) between 2019 and 2020. The questionnaires collected data on the clinical characteristics of SB, and female sexual function was assessed using the 6-item version of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6) validated to Portuguese and Spanish.
Half of the patients had had sexual activity at least once in the life, but most (57.1%) did not use any contraception method. Sexual dysfunction was present in most (84.3%) patients, and all sexual function domains were impaired compared those of non-neurogenic women. The presence of urinary and fecal incontinence significantly affected the quality of their sexual activity based on the FSFI-6.
The specific clinical aspects of the SB patients, such as urinary and fecal incontinence, should be properly addressed by their doctors, since they are associated with reduced sexual activity and lower FSFI-6 scores in the overall or specific domains. There is also a need to improve gynecological care among sexually-active SB patients, since most do not use any contraceptive methods and are at risk of inadvertent pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):731-738
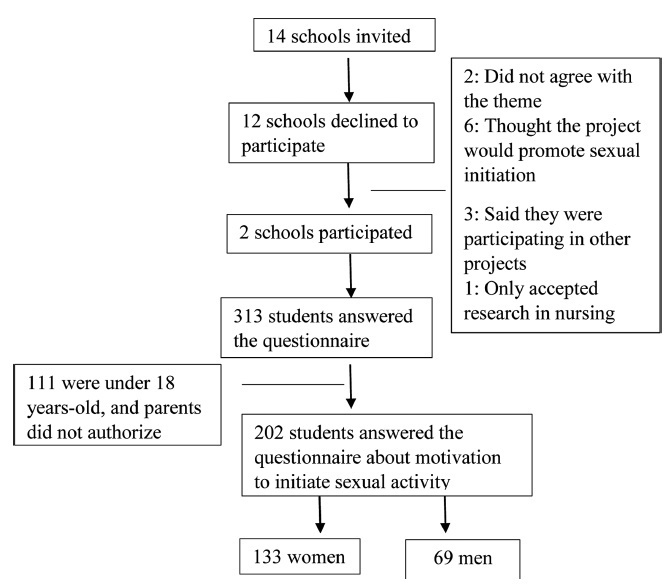
Adolescence is characterized by significant biological and psychological changes. During this time, the increased production of androgens leads to increased sexual behavior, and this may contribute to early initiation of sexual activity. The objectives of the present cross-sectional study of adolescents enrolled in state schools in the city of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil, were to determine the average age at the first sexual intercourse (sexarche), the average number of sexual partners, and the frequency of contraceptive and condom use. Information on the age at sexarche, number of sexual partners, use of different contraceptive methods, and use of condoms were obtained using a semistructured questionnaire. Quantitative variables are expressed as means and standard deviations (SDs), and qualitative variables as absolute and relative frequencies. The chi-squared test was used for comparisons of qualitative variables, and the Student t-test for comparisons of continuous variables. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS (version 9.4, North Carolina State University, USA). We evaluated 202 students who answered the questionnaire, 69 males (36.36%) and 133 females (63.64%). The age at sexarche for men ranged from 7 to 18 years old, and for women from 7 to 17 years old. Forty-eight girls (36.01%) and 21 boys (30.43%) were in the first year of high school, 66.94% of adolescents reported sexual intercourse, and 56.25% used a condom during the first sexual intercourse. A total of 36.72% of students said they had safe sex most of the time, and 83.59% said that the first sexual intercourse happened because they “had a crush on” the other person.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):26-34
To assess the construct and criterion validity of the Postmenopause Sexuality Questionnaire (PMSQ).
The present methodological questionnaire validation study included postmenopausal women. The construct validity was tested by factor analysis and the criterion validity was performed using the correlation between the PMSQ and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). The ROC curve was used to verify sensitivity, specificity and to determine the cutoff point of the PMSQ.
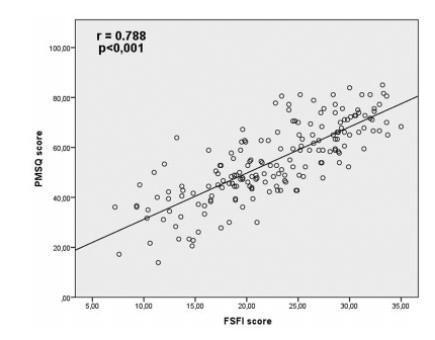
A total of 181 women with amean age of 56.4 ± 5.7 years old were evaluated. The exploratory factor analysis showed that the PMSQ presented Kaiser test = 0.88 and χ2 = 3293.7 (p < 0.001), commonalities ≥ 0.5, and extraction of 9 factors with eigenvalue ≥ 1; explaining 66.3% of the total variance. The PMSQ presented factor loadings between 0.4 and 0.8. A strong correlation between the 2 questionnaires (r = 0.79; p = 0.000) was shown. The cutoff point of the PMSQ was ≤ 55.5, assuming 87.9% sensitivity and 78.9% specificity (p < 0.001).
Since the PMSQ showed a strong correlation with the FSFI questionnaire, it presented good psychometric properties to assess the sexuality in postmenopausal women. Based on these results, the PMSQ could be widely tested as a specific instrument to examine the sexual function in postmenopausal women. Future studies, designed to examine the PMSQ instrument in different populations, are needed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):555-563
To determine the prevalence of sexual dysfunction and its associated factors in pregnant women.
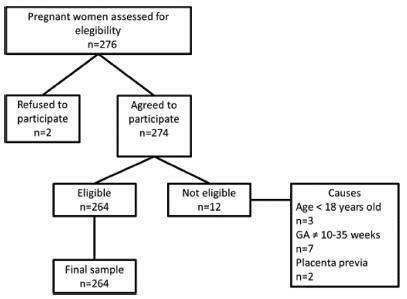
A descriptive, cross-sectional study including 262 pregnant women aged 18 years or older with gestational age between 10 and 35 weeks. Women with urinary tract infections and conditions of gestational risk were excluded. The Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) questionnaire was used. We performed a univariate descriptive analysis, and comparisons between the mean values of the sexual function domains were made using the Student t-test. The chi-squared test was used to determine the association between the independent and dependent variables. The prevalence ratios, with their respective 95% confidence intervals, were also estimated, and a multivariate analysis was performed.
A total of 64.9% of women reported a decrease in the frequency of sexual activity during pregnancy. Slightly more than half of the women (50.8%) were satisfied, and arousal was reported as excellent/good by 30.5% of them. The frequency of sexual difficulties/dysfunctions increased with pregnancy, rising from 5.7% to 58.8%, and pain during sexual intercourse was reported by 45.8% of them. Having higher education degree decreased the chance of being sexually dissatisfied by 50%. The total PSRI score showed a significant decrease from the prepregnancy period (mean score = 89.8, “excellent”) to the pregnancy period (mean score = 59.2, “good”).
The mean sexual function score during pregnancy was classified as good, although most pregnant women reported at least one type of alteration in the sexual function domains, and the report of dissatisfaction was more frequent in women with lower schooling.