Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):9-13
We evaluated risk factors to determine if there were specific risk factors that could predict massive bleeding in nulliparous women with placenta previa.
The participants were classified into two groups. Women with a calculated blood loss ≥ 1,000mL were included in the massive bleeding group. Women without any signs or symptoms related with hypovolemia or with a calculated bleeding volume < 1,000 mL were categorized into the non-massive bleeding group.
There were 28 patients (40.6%) with massive bleeding and 41 cases (59.4%) with non-massive bleeding. The calculated blood loss and number of cases that required red cell transfusions were statistically different between the groups (< 0.005 and 0.002, respectively). There were no statistically significant differences in terms of maternal or fetal factors, placental location, or delivery characteristics between the two groups.
We could not determine the predictive features for massive hemorrhage based on clinical features, delivery features, or placental location.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):9-19
To present and validate a multifunctional electronic medical record (EMR) for outpatient care to women with endocrine disorders in pregnancy and to compare health information data fill rate to conventional medical records.
We developed an EMR named Ambulatory of Endocrine Diseases in Pregnancy (AMBEG) for systematic registration of health information The AMBEG was used for obstetric and endocrine care in a sample of pregnant women admitted to the maternity reference in high-risk pregnancies in Bahia from January 2010 to December 2013. We randomly selected 100 patients accompanied with AMBEG and 100 patients monitored with conventional consultation and compared the health information data fill rate of the electronic consultation to that performed using conventional medical records.
1461 consultations were held, of which 253, 963 and 245 were first, follow-up and puerperium consultations, respectively. Most patients were pregnant women with diabetes (77.2%) and 60.1% were women with pre-gestational diabetes. The AMBEG satisfactorily replaced the conventional medical record. The percentage of registered information was significantly higher in the AMBEG: clinical symptoms (87% versus 100, p < 0.01), uterine height (89 versus 75%, p = 0.01), total weight gain (91 versus 40%, p < 0.01) and specific diabetes data (diet, insulin regimen, glycemic control and management of hypoglycemia) revealed a significant difference (p < 0.01). The ability to export data to worksheets greatly facilitated and accelerated the statistical analysis of the data.
AMBEG is a useful tool in clinical care for women with endocrine diseases during pregnancy. The fill rate of clinical information was superior to that registered in conventional medical records.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):9-13
To evaluate the prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) in fetuses of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in the beginning of the treatment.
A cross-sectional study was performed between July 1, 2013, and Decem-ber 20, 2013, in a public maternity clinic in southern Brazil. The subjects were 63 fetuses of mothers with gestational diabetes, with a single pregnancy and no other associated pathologies. We diagnosed HCM through a fetal echocardiography before treatment and evaluated the maternal and fetal characteristics.
The average age of the pregnant women was 32.32 (±6.2) years, and the average gestational age at the time of the evaluation was 30.59 (±2.27) weeks. The interventricular septum thickness showed a standard deviation of more than two in 50.8% of the fetuses (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 38.1-63.5%). The left ventricular wall thickness showed a standard deviation of more than 2 in 13 (20.6%) fetuses (95%CI: 11.1-30.2%). The HCM was confirmed in 54% of the fetuses (95%CI: 41.3-65.1%). The fetal abdominal circumference was normal in 46 (73%) fetuses, and 50% of these fetuses had HCM.
The prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in fetuses of pregnant women with GDM before treatment was of 54% (95%CI: 41.3-65.1%).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(1):9-14
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000100002
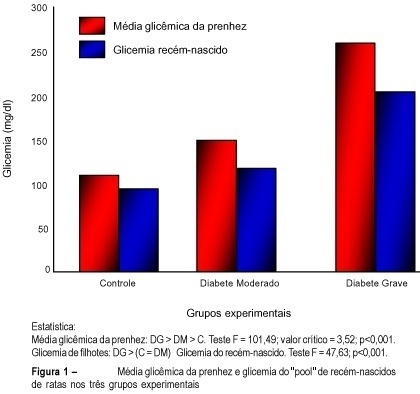
Purpose: to evaluate the effects of maternal diabetes on the fetal lung phospholipid profiles of rats with moderate and severe diabetes measuring lecithin (L), sphingomyelin (S), phosphatidyl-glycerol (PG), phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), and the relationships between L/S and PG/PI. Methods: fifty-four mature Wistar rats were submitted to experimental diabetes and pregnancy¹. Diabetes was induced by alloxan (42 mg/kg of weight, iv) and three groups were formed: control; moderate diabetes (MD), with glycemia levels between 120 and 200 mg/dl, and severe diabetes (SD), with glycemia levels higher than 200 mg/dl. On the 21st day, cesarian section was performed, and the fetal lungs were macerated and pooled. The phospholipids were measured by unidirectional thin-layer chromatography. Results: 1) the fetal lungs of the rats with moderate diabetes showed higher weight (0.159 g) and lower concentration of PG (3.0 µg/ml) and PI (3.4 µg/ml) than the controls, and the same relationship between L/S (2.2) and PG/PI (2.0). The fetal lungs of the rats with severe diabetes showed lower weight (0.145 g), the same values of L/S (1.9) and PG/PI (2.1), and lower PI (5.1 µg/ml) value than the controls. Conclusions: 1) the pulmonary maturity retardation in the pups of rats with moderate diabetes is explained by the higher pulmonary weight associated with lower concentration of PG and PI; 2) the pulmonary maturity acceleration in the pups of rats with severe diabetes is explained by the lower pulmonary weight associated with the same concentration of PG and PI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):9-13
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100002
PURPOSE: to compare maternal and neonatal outcomes between spontaneous vaginal and Simpson-Braun forceps deliveries in nulliparous women. METHOD: a retrospective study including two groups of nulliparous women, who had vaginal delivery under peridural anesthesia in the obstetric unit of the CAISM-UNICAMP: the forceps group included 119 women who had Simpson-Braun forceps delivery, and the normal group included 114 women who delivered spontaneously. Neonatal outcomes, such as Apgar score and the evolution in the first days of life, were studied. Data were compared in both groups and, for statistical analysis, c² test, Fisher exact, and Student t tests were used. The differences were considered significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: the indications for Simpson-Braun forceps delivery were maternal-fetal relief (90 cases) and abbreviation of the expulsive period (29 cases). In the forceps group there were 8 cases (6.7%) of vaginal injuries; a similar result was observed in the normal group. The number of hospitalization days for the parturient and the newborns was identical, 2.4 days. The newborns in the two groups had similar Apgar scores inferior to 7 at the first minute (7.5 vs 4.3%) and at the fifth minute (1.6 vs1.7%). The weight in the two groups had similar results (3,146 and 3,016 g). The first days of life did not differ between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: the use of Simpson-Braun forceps was safe, when compared to spontaneous vaginal delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):90-96
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200008
To evaluate the frequency of sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea,
restless leg syndrome and insomnia in overweight/obese postmenopausal women seen
in a climacteric sleep disorders clinic.
Thirty-four postmenopausal women were selected using the following inclusion
criteria: age between 50 and 70 years; at least 12 months of amenorrhea; body mass
index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25 kg/m2; and sleep-related
complaints with at least one previous polysomnography. Patients provided responses
to 6 questionnaires related to sleep characteristics and menopausal symptoms.
Weight and height were measured using standardized scales, and abdomen and hip
circumferences were also measured. The statistical analyses were performed using
the χ2 test for qualitative variables and using Student's t-test for
quantitative variables.
Patients' characteristics were as follows: mean age of 60.35 years; mean BMI of
31.62; an average of 11.61 postmenopausal years and an average Kupperman Index of
19. A total of 85.2% of the patients had a waist/hip ratio of less than 0.8. The
Epworth Scale score was greater than or equal to 9 in 50% of patients; 68% had
sleep disturbances according to the Pittsburgh Index, and 68% were classified as
high-risk for sleep apnea by the Berlin Questionnaire. On polysomnography, 70.58%
of the patients had a sleep efficiency lower than 85%; 79.41% had a sleep latency
of less than 30 min; 58.82% had a REM sleep latency of less than 90 min, and
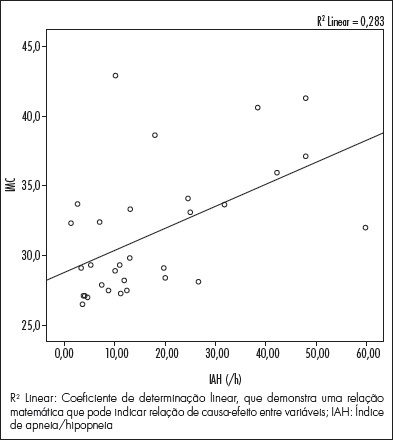
44.11% had mild apnea. When the groups were compared, a linear association was
identified between BMI and the AHI average, and a relationship between high BMI
and use of drugs for thyroid treatment was found.
There was a high prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing, initial insomnia,
fragmented sleep, and thyroid disorders in the group with higher BMI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):90-95
To describe clinical and sociodemographic characteristics of women with deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) and assess their quality of life (QOL) during 6 months of medical treatment.
A descriptive cross-sectional study of 60 women diagnosed with DIE either by surgery or image methods (ultrasound or magnetic resonance), who received clinical treatment for at least 6 months in the Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Both the SF-36 and the EHP-30 questionnaires were used to assess the quality of life.
The mean age of the patients was 37.7 ± 6.0 years old, with 50% presenting dysmenorrhea; 57% dyspareunia; and 50% chronic pelvic pain. The SF-36 and the EHP-30 revealed impaired quality of life. In the SF-36, the worst domains were limitation due to emotional aspects (40.2 ± 43.1) and self-esteem and disposition (46.1 ± 24.8), whereas in the EHP-30 they were social well-being (50.3 ± 30.6); infertility (48.0 ± 36.3); and sexual intercourse (54.0 ± 32.1).
Although clinically treated, women with deep endometriosis present impairment in different domains of quality of life regardless of the questionnaire used for evaluation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
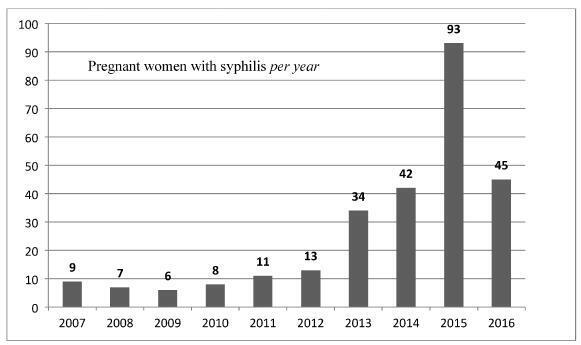
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births - this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.