Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):870-877
To determine the association between maternal mobile phone use and adverse outcomes in infants, children, and mothers.
In March 202, we conducted a search on the MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus databases. Data extraction and an assessment of the quality of the studies were performed by two authors. The quality of the studies was assessed using the checklist of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
Studies assessing behavioral problems in infants aged 6 to 18 months reported null findings. However, an increased risk of emotional and behavioral disorders was observed in children aged between 7 and 11 years whose mothers had been exposed to cell phones. The findings regarding the association between maternal cell phone exposure and adverse outcomes in children aged 3 to 5 are controversial. A study found a significant association between the call time (p=0.002) or the history of mobile phone use (in months) and speech disorders in the children (p=0.003). However, another study found that maternal cell phone use during pregnancy was not significantly associated with child psychomotor and mental developments. Inconclusive results were observed about the adverse outcomes in fetuses, such as fetal growth restriction or t scores for birth weight in cell phone users as opposed to non-users. On the contrary, the children ofmothers who were cell phone users had a lower risk of scoring low on motor skills. Similar results were observed regarding the adverse outcomes of cell phone use in infants, such as fetal growth restriction or low birth weight, and the risk of preeclampsia was lower among subjects with medium and high cell phone exposure, as opposed to those with low exposure.
Studies on behavioral problems have reported different postnatal results, such as null findings among infants and a positive association in children.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):871-877
This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic profile of breast cancer cases during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic compared with the previous year.
It is a retrospective study of cases diagnosed by a reference service in the public health system of Campinas, SP, Brazil. Two periods were analyzed: March to October 2019 (preCOVID period) and March to October 2020 (COVID-period). All women diagnosed during the periods were included. The Chi-Squared or Fisher exact and Mann-Whitney tests were used.
In the preCOVID and COVID periods, breast cancers were diagnosed, respectively, in 115 vs 59 women, and the mean ages at diagnosis were 55 and 57 years (p = 0.339). In the COVID period, the family history of breast cancer was more observed (9.6% vs 29.8%, p < 0.001), cases were more frequently symptomatic (50.4% vs 79.7%, p < 0.001) and had more frequently palpable masses (56.5% vs 79.7%, p = 0.003). In symptomatic women, the mean number of days from symptom to mammography were 233.6 (458.3) in 2019 and 152.1 (151.5) in 2020 (p = 0.871). Among invasive tumors, the proportion of breast cancers in stages I and II was slightly higher in the COVID period, although not significantly (76.7% vs 82.4%, p = 0.428). Also in the COVID period, the frequency of luminal A-like tumors was lower (29.2% vs 11.8%, p = 0.018), of triple-negative tumors was twice as high (10.1% vs 21.6%, p = 0.062), and of estrogen receptor-positive tumors was lower (82.2% vs 66.0%, p = 0.030).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, breast cancer diagnoses were reduced. Cases detected were suggestive of a worse prognosis: symptomatic women with palpable masses and more aggressive subtypes. Indolent tumors were those more sensitive to the interruption in screening.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):878-883
It is a challenge to consider preeclampsia (PE) diagnosis and management in low and middle-income settings, where it represents a major public health concern. The placenta is the underlying cause of disease, and the plasma concentrations of proangiogenic and antiangiogenic factors released by the placenta can reflect the risks of disease progression. Antiangiogenic proteins, such as soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1), and proangiogenic, like placental growth factors (PlGF), are directly and inversely correlated with the disease onset, respectively.
Narrative review on the use of biomarkers (sFlt-1 to PlGF ratio) with a suggested guidance protocol.
Key considerations on the use of biomarkers: the sFlt-1/PlGF ratio is mainly relevant to rule out PE between 20 and 36 6/7 weeks in cases of suspected PE; however, it should not replace the routine exams for the diagnosis of PE. The sFlt-1/PlGF ratio should not be performed after confirmed PE diagnosis (only in research settings). In women with suspected PE, sFlt-1/PlGF ratio < 38 can rule out the diagnosis of PE for 1 week (VPN = 99.3) and up to 4 weeks (VPN= 94.3); sFlt-1/PlGF ratio > 38 does not confirm the diagnosis of PE; however, it can assist clinical management. In cases of severe hypertension and/or symptoms (imminent eclampsia), hospitalization is imperative, regardless of the result of the sFlt-1/PlGF ratio.
The use of biomarkers can help support clinical decisions on the management of suspected PE cases, especially to rule out PE diagnosis, thus avoiding unnecessary interventions, especially hospitalizations and elective prematurity

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):878-882
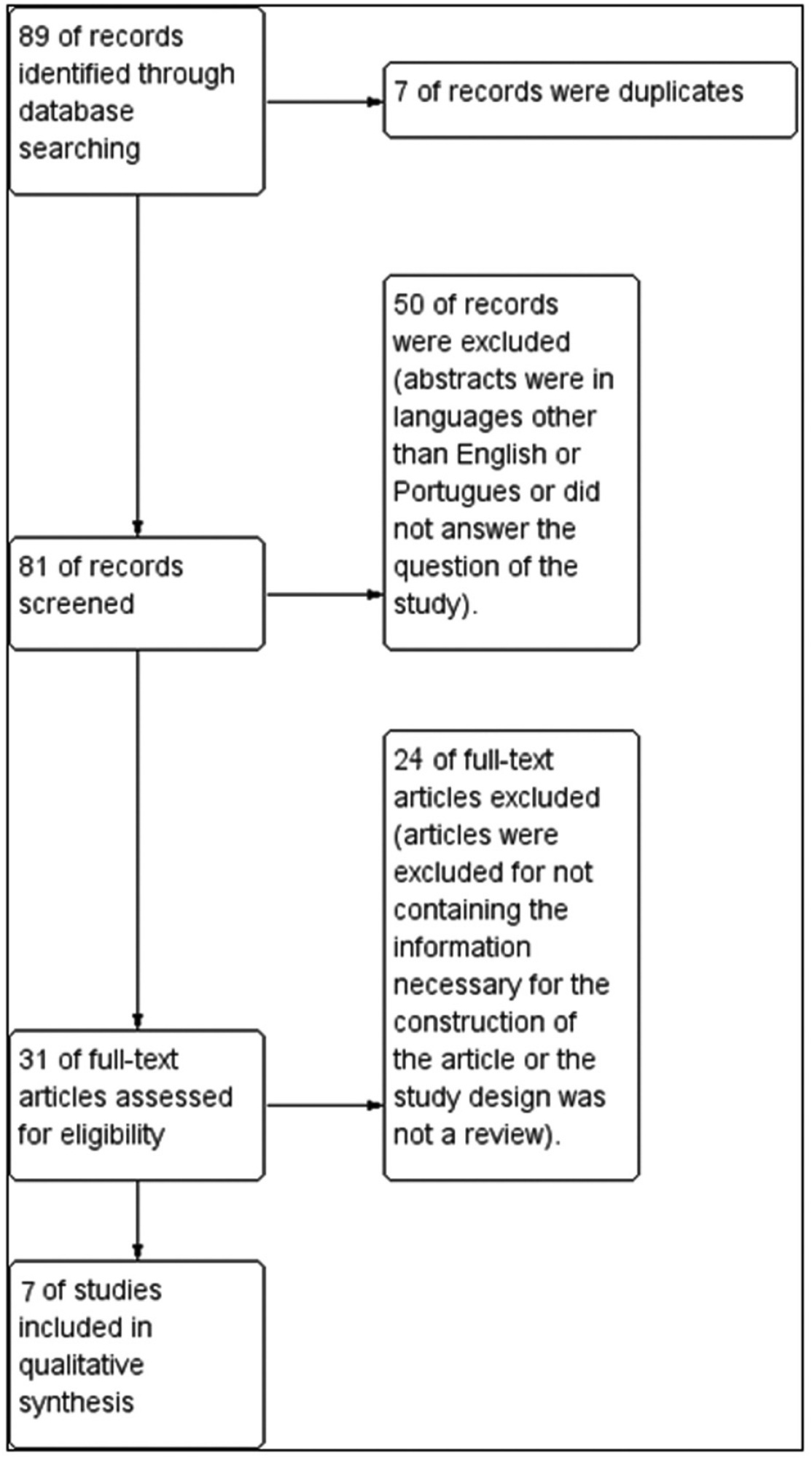
Non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (niPGT-A) aiming to assess cell-free embryonic DNA in spent culturemedia is promising, especially because it might overcome the diminished rates of implantation caused by the inadequate performance of trophectoderm (TE) biopsy. Our center is part of the largest study to date assessing the concordance between conventional PGT-A and niPGT-A, and we report here the delivery of the first baby born in Brazil using niPGT-A. The parents of the baby were admitted to our center in 2018. They did not present history of infertility, and they were interested in using in vitro fertilization (IVF) and PGT-A in order to avoid congenital anomalies in the offspring. A total of 11 (3 day-5 and 8 day-6) expanded blastocysts were biopsied, and the spent culture media (culture from day-4 to day-6) from 8 day-6 blastocysts were collected for niPGT-A. Overall, 7 embryos yielded informative results for trophectoderm (TE) and media samples. Among the embryos with informative results, 5 presented concordant diagnosis between conventional PGTA and niPGT-A, and 2 presented discordant diagnosis (1 false-positive and one falsenegative). The Blastocyst 4, diagnosed as 46, XY by both niPGT-A and conventional PGTA, was warmed up and transferred, resulting in the birth of a healthy 3.8 kg boy in February 2020. Based on our results and the recent literature, we believe that the safest current application of niPGT-A would be as a method of embryo selection for patients without an indication for conventional PGT-A. The approximate 80% of reliability of niPGT-A in the diagnosis of ploidy is superior to predictions provided by other noninvasive approaches like morphology and morphokinetics selection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):88-93
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200007
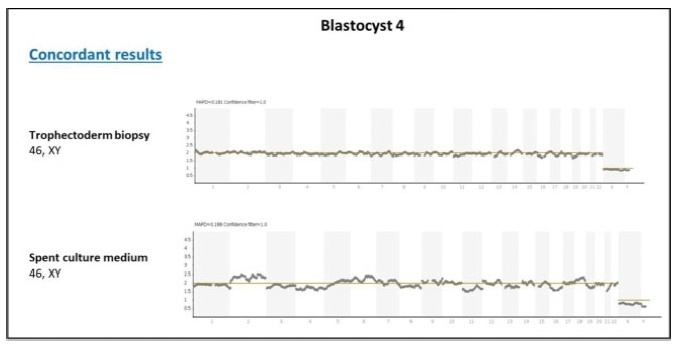
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of the prolonged use of a high dose of tibolone on the body weight variation and lipid profile of oophorectomized female rats. METHODS: 15 Wistar rats weighing 250 g were randomly divided into two groups. The Experimental Group (n=9) received 1 mg/day of oral tibolone. The Control Group (n=6) received daily 0.5 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose by gavage. Bilateral oophorectomy was performed 30 days before the beginning of the experiment. On day 0 of the experiment, the animals began to receive the respective treatment for 20 weeks. Body weight was controlled every seven days and food consumption was measured every three to four days along the experiment, in order to establish the daily mean consumption per animal. The results were compared by the Student's t-test, with the significance level set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the daily food consumption of the Tibolone Group was significantly lower (12.7±1.2 g, p<0.001) compared to the Control Group (14.5±1.4 g). This difference was also significant when the body weight was compared between the Tibolone and Control Groups (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group having lower weight along the experiment. At the end of the experiment, the mean body weight was 215.6±9.3 g in the Tibolone Group and 243.6±6.4 g in the Control Group. Regarding the lipid profile, the Tibolone Group had significantly (p<0.001) lower total cholesterol compared to the Control Group (30.3 versus 78.6 mg/dL). The level of HDL-c was also significantly different (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group showing lower levels than the Control Group (9.0 versus 52.0 mg/dL). No significant difference between the groups was registered in the other biochemical parameters examined (LDL-c, VLDL-c and triglycerides). CONCLUSIONS: tibolone causes a significant reduction of HDL-c and total cholesterol and has a deleterious effect on the body weight of oophorectomized rats, which may be related to the lower food ingestion by these animals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):88-96
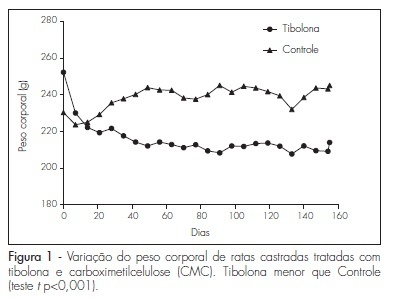
The objective of the study is to describe the process of translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Lymphoedema Functioning, Disability, and Health Questionnaire for Lower Limb Lymphoedema (Lymph-ICF-LL) into (Brazilian) Portuguese.
The process was comprised of five steps - translation, back translation, revision by an expert panel, pretest, and final translation. The first translation was performed by two professionals of the healthcare area, and the back translation was performed by two translators. An expert panel assessed the questions for semantics and idiomatic, cultural, and conceptual equivalence. The pretest was conducted on 10 patients with lymphedema.
Small differences were identified between the translated and back-translated versions, which were revised by the expert panel. The patients included in the pretest found 10 questions difficult to understand; these questions were reassessed by the same expert panel.
The results of the translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Lymph- ICF-LL resulted in a Brazilian Portuguese version, which still requires validation with various samples of the local population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):883-884
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):884-890
Although almost 0.7% of the Brazilian population identifies as transgender, there is currently no training for healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care to these patients, including the discussion of reproductive planning. The use of testosterone promotes amenorrhea in the first months of use; however, this effect does not guarantee contraceptive efficacy, and, consequently, increases the risks of unplanned pregnancy. The present article is an integrative review with the objective of evaluating and organizing the approach of contraceptive counseling for the transgender population who were assigned female at birth. We used the PubMed and Embase databases for our search, as well as international guidelines on care for the transgender population. Of 88 articles, 7 were used to develop the contraceptive counseling model. The model follows the following steps: 1. Addressing the information related to the need for contraception; 2. Evaluation of contraindications to the use of contraceptive methods (hormonal and nonhormonal); and 3. Side effects and possible discomfort associated with the use of contraception. The contraceptive counseling model is composed of 18 questions that address the indications and contraindications to the use of these methods, and a flowchart to assist patients in choosing a method that suits their needs.