Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):803-807
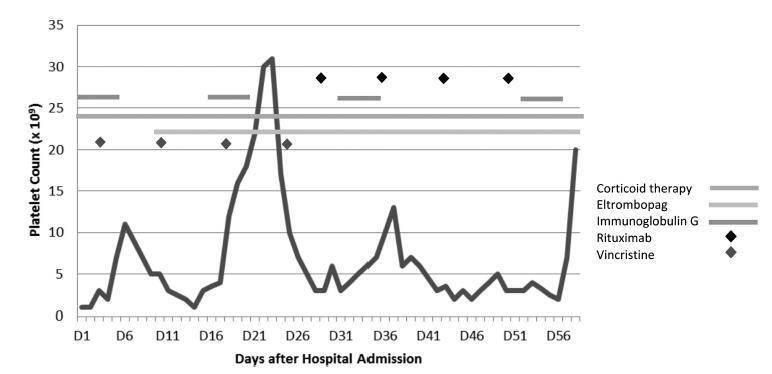
Thrombocytopenia is the most common hemostatic change in pregnancy, but severe thrombocytopenia is rare. One of the causes, immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), is characterized by increased platelet destruction by immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies, presenting a high risk of hemorrhage for the patient, but also for the fetus, since antibodiesmay cross the placenta.We present the case of a 23-year-old pregnant woman with a history of Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the mandible submitted to surgery and chemotherapy when she was 10 years old, with diagnosis of ITP since then. At 28 weeks of gestation, she presented with petechiae, epistaxis, and gingival bleeding, with a platelet count of 3 x 109/L and positive IgG antiplatelet antibodies test. At a multidisciplinary discussion, it was decided to delay a cesarean section, due to the absence of fetal distress and to the high risk of morbidity for the patient. Many therapies were attempted without success. The IgG produced a slight and transient increase in the platelet count. On the 36th week of gestation, an elective cesarean section was performed. The perioperative period transfusions were guided by rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) monitoring. The procedure was performed under general anesthesia and videolaryngoscopy-assisted intubation. The patient was hemodynamically stable, without significant bleeding, and was transferred to the intensive care unit. The platelet count eventually decreased and a splenectomy was performed. Regional anesthesia may be contraindicated, and general anesthesia is associated with an increased risk of airway hemorrhage due to traumatic injury during the tracheal intubation and of hemorrhage associated with the surgical procedure. A multidisciplinary approach is essential in high-risk cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):803-804
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):804-805
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):805-810
The aim of the present study was to examine the relation between the PON1 polymorphisms and recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
In a cross-sectional study, blood samples were collected from 100 females. DNA was extracted and PON1 genotypes were determined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification.
Regarding PON1 L55M, the mutated allele (M) frequency was found in 70.5% in RPL and in 53.5% in controls; theMallele was significantly associated with an increased risk of RPL (adjusted odds ratio [ORadj]=2.07; 95% confidence interval [CI]; p<0.001). However, regarding PON1 Q192R, the R mutated allele frequency was found in 28.5% in RPL and in 33% in controls. The R allele did not show any risk for RPL (ORadj 0.81; 95%CI; p=0.329).
The present study suggests that there is an effect of genetic polymorphism on RPL and provides additional evidence that combines with the growing information about the ways in which certain PON1 genotypes can affect the development of the fetus in the uterus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):805-810
To analyze the most frequent referrals for fetal echocardiography, including advanced maternal age and its association with abnormal results.
We included all pregnant women referred to perform fetal echocardiography (gestational age 22-32 weeks) in 2 health centers in Rio de Janeiro, from June 2015 to June 2016. Advanced maternal age was considered when age was > 35 years at the time of delivery). Referral reasons and results were recorded, according to the Brazilian Fetal Cardiology Statement. Crude and adjusted prevalence ratios were calculated (Poisson regression). We considered p < 0.05 as significant.
A total of 1,221 tests were analyzed. Abnormal fetal echocardiography was observed in 14.82% of the cases. The most frequent abnormalities were interventricular septal defect (6.39%), septal hypertrophy (3.35%) and atrioventricular septal defect (1.14%). Routine exams were performed in 559 women, 289 were referred for advanced maternal age and 373 were referred according to the Brazilian FetalCardiology Statement criteria. An obstetric ultrasound suggesting fetal cardiacabnormality, maternal diabetes, increased nuchal translucency, and obstetric ultrasound suggesting a noncardiac abnormality were strongly associated with an abnormal fetal echocardiography. Abnormal results were not more frequent in women with advanced maternal age when compared with the rest of the study group.
It was observed that routine exams and advancedmaternal age referrals were very frequent. Those exams were not associated to fetal echocardiography abnormalities. In this scenario, when the obstetric ultrasound suggests a fetal cardiac
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):806-817
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):807-812
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004001000008
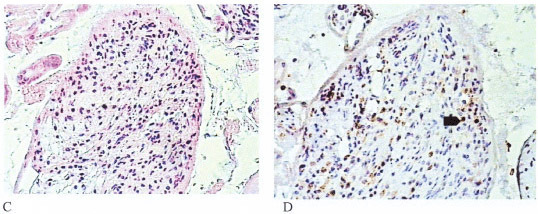
PURPOSE: placental villitis has been correlated with perinatal infection, although a percentage of cases remains etiologically unknown. The present study was aimed at the systematic morphological study of placentas for imunohistochemical characterization of villitis and assessment of its possible correlation with maternal and fetal outcome. METHODS: a hundred and twenty-eight placentas were studied. Gross examination was performed and all collected fragments were analyzed microscopically by the hematoxylin-eosin method. Villits was classified according to the inflammatory degree in to mild, moderate and severe. The immunohistochemical study to identify infectious agents was performed using monoclonal antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Cytomegalovirus. For inflammatory cell phenotype identification monoclonal antibodies against CD68, CD57, CD3, and CD20 were used. Statistical analysis was performed with the variables: maternal age and fetal gestational age, fetal and placental weight, and fetal and maternal outcomes. To compare the two groups we used the Mann-Whitney test and for proportions we used the chi2 test. The differences in the mean values between the treatment groups were considered statistically significant when p<0.05 (5%). RESULTS: villitis was identified in 11.7% of the cases. In 40% of the cases the children were stillborn (p=0.003). One case showed positive staining for toxoplasmosis while the remaining cases were negative. Imunohistochemical staining showed CD68+ cells, PanT+ cells and negative CD57 and PanB cells. CONCLUSION: we concluded that the intensity of the inflammatory process in the placenta was correlated with the severity of the fetal disease. The inflammatory cells in the villitis focus were macrophages; however, we could not identify infectious agents correlated with the villitis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):808-817
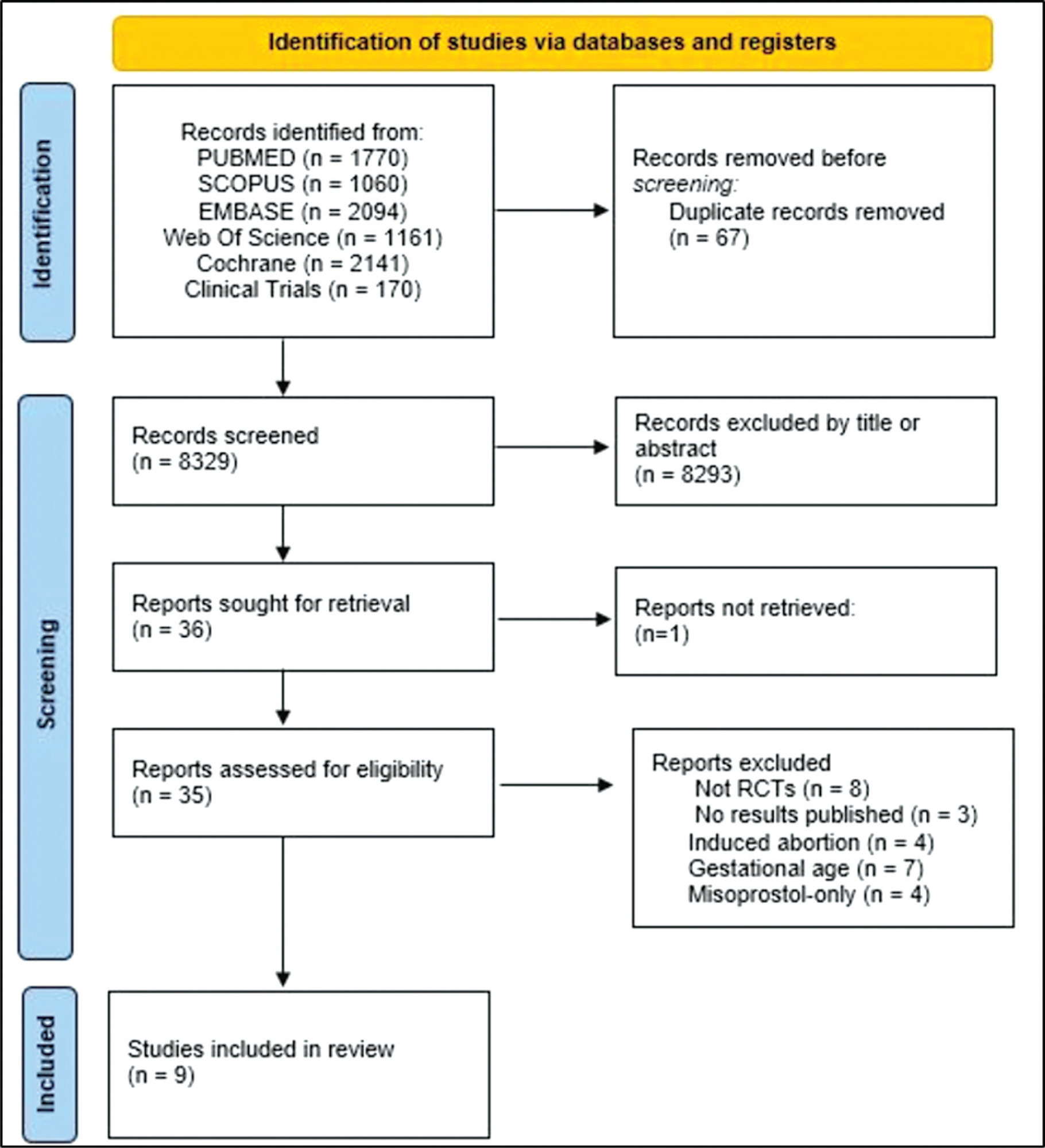
To assess the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of misoprostol in the treatment of incomplete miscarriage.
The PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases (clinicaltrials.gov) were searched for the relevant articles, and search strategies were developed using a combination of thematic Medical Subject Headings terms and text words. The last search was conducted on July 4, 2022. No language restrictions were applied.
Randomized clinical trials with patients of gestational age up to 6/7 weeks with a diagnosis of incomplete abortion and who were managed with at least 1 of the 3 types of treatment studied were included. A total of 8,087 studies were screened.
Data were synthesized using the statistical package Review Manager V.5.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). For dichotomous outcomes, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were derived for each study. Heterogeneity between the trial results was evaluated using the standard test, I2 statistic.
When comparing misoprostol with medical vacuum aspiration (MVA), the rate of complete abortion was higher in the MVA group (OR = 0.16; 95%CI = 0.07–0.36). Hemorrhage or heavy bleeding was more common in the misoprostol group (OR = 3.00; 95%CI = 1.96–4.59), but pain after treatment was more common in patients treated with MVA (OR = 0.65; 95%CI = 0.52–0.80). No statistically significant differences were observed in the general acceptability of the treatments.
Misoprostol has been determined as a safe option with good acceptance by patients.