You searched for:"Antonio Fernandes Moron"
We found (34) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):475-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700003
PURPOSE: to study the effects of low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives (OHC) (<30 mg of ethynylestradiol) on the intraerythrocytic folate levels. METHODS: this was a prospective transversal study with 95 patients treated in the Family Planning Clinic of UNIFESP (Federal University of São Paulo). The control group (Condom group) consisted of patients using condom as their exclusive contraceptive method during the last 12 months, and the study groups consisted of patients using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives, in the following way: OHC 3 group (three to six months of use), OHC 6 group (six to twelve months of use) and OHC 12 group (more than twelve months of use). Intraerythrocytic folate was determined by the ionic capture method. Analysis of variance and c² test were used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the Condom group showed a rate of 44% of patients with folate lower than 186.0 ng/mL and the users of low-dose oral contraceptives showed a rate of 32% (OHC 3 group), 16% (OHC 6 group) and 31% (OHC 12 group). We did not find in the group using low-dose oral contraceptives a significant reduction in the average level of intraerythrocytic folate compared to the control group and there was no statistically significant difference (p=0.28) regarding time of use. CONCLUSION: we observed reduced levels of intraerythrocytic folate in a significant number (44%) of patients not using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives. Their rates were similar to the lower limit considered to be normal by most authors, which points to a basal folate deficiency in the studied group. We did not observe any alteration in the level of intraerythrocytic folate in patients using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):499-503
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the embryo's volume (EV) between the seventh and the tenth gestational week, through tridimensional ultrasonography. METHODS: a transversal study with 63 normal pregnant women between the seventh and the tenth gestational week. The ultrasonographical exams have been performed with a volumetric abdominal transducer. Virtual Organ Computer-aided Analysis (VOCAL) has been used to calculate EV, with a rotation angle of 12º and a delimitation of 15 sequential slides. The average, median, standard deviation and maximum and minimum values have been calculated for the EV in all the gestational ages. A dispersion graphic has been drawn to assess the correlation between EV and the craniogluteal length (CGL), the adjustment being done by the determination coefficient (R²). To determine EV's reference intervals as a function of the CGL, the following formula was used: percentile=EV+K versus SD, with K=1.96. RESULTS: CGL has varied from 9.0 to 39.7 mm, with an average of 23.9 mm (±7.9 mm), while EV has varied from 0.1 to 7.6 cm³, with an average of 2.7 cm³ (±3.2 cm³). EV was highly correlated to CGL, the best adjustment being obtained with quadratic regression (EV=0.2-0.055 versus CGL+0.005 versus CGL²; R²=0.8). The average EV has varied from 0.1 (-0.3 to 0.5 cm³) to 6.7 cm³ (3.8 to 9.7 cm³) within the interval of 9 to 40 mm of CGL. EV has increased 67 times in this interval, while CGL, only 4.4 times. CONCLUSIONS: EV is a more sensitive parameter than CGL to evaluate embryo growth between the seventh and the tenth week of gestation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):5-11
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100002
PURPOSE: to study the value of Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus, between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, associated to the nuchal translucency thickness measurement, in the detection of adverse fetal outcome. METHODS: a transversal and prospective study in which a total of 1,268 fetuses were studied consecutively. In 56 cases, a cytogenetic study was performed on material obtained from a biopsy of the chorionic villus and, in 1,181 cases, the postnatal phenotype was used as a basis for the result. In addition to the routine ultrasonographic examination, all the fetuses were submitted to measurement of the nuchal translucency thickness and to Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus. Aiming at prevalence and accuracy indices, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, probability of false-positive, probability of false-negative, reason of positive probability and reason of negative probability were calculated and analyzed. RESULTS: from the total of 1,268 fetuses, 1,183 cases were selected for analysis. From this number, 1,170 fetuses were normal (98.9%) and 13 fetuses presented adverse outcome at birth (1.1%), including fetal death (trisomy 21 and 22) in two cases; genetic syndrome (Nooman) in one case; two cases of polymalformed fetuses; cardiopathy in three cases; and other structural defects in five cases. The prevalence of the modified ductus venosus (wave A zero/reverse) in the studied population was of 14 cases (1.2%), with a false-positive rate of 0.7%. CONCLUSIONS: there is a significant correlation between the alteration of the ductus venosus Doppler velocimetry and the thickness of the nuchal translucency as an ultrasonographic marker for the first trimester of gestation, in the detection of adverse fetal outcome, especially serious malformations. The ductus venosus was able to diminish the false-positive result in comparison to the isolated use of the nuchal translucency thickness, improving considerably the positive predictive value of the test.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):527-533
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of hysterosalpingography (HSG) and transvaginal sonography (TVS) in terms of detecting uterovaginal anomalies in women with a history of recurrent miscarriage. METHODS: eighty patients who presented two or more consecutive miscarriages were submitted to HSG, TVS and hysteroscopy (HSC). The following diagnoses were considered separately: uterine malformations, intrauterine adhesions and polypoid lesions. Hysteroscopy was the gold standard. The matching among the different methods was evaluated by the kappa coefficient and its significance was tested. The significance level was 0.05 (alpha=5%). Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, with 95% of statistical confidence interval, were calculated. RESULTS: uterovaginal anomalies were detected in 29 (36.3%) patients: 11 (13.7%) were uterine malformations, 17 (21.3%) intrauterine adhesions and one (1.3%) a polypoid lesion. The global matching between HSG and HSC was 85.5%, while between TVS and HSC it was only 78.7%. The best accuracy of HSG appeared to be for the diagnosis of uterine malformations and intrauterine adhesions (diagnostic accuracy of 97.5 and 95%, respectively). For the diagnosis of polypoid lesions, HSG had a diagnostic accuracy of only 92.5%, due to the low rate of positive predictive value (14.3%). TVS had a worse accuracy for all diagnoses, 93.7% for the diagnosis of uterine malformations and 85% for intrauterine adhesions, due to low sensitivity. CONCLUSIONS: histerosalpingography showed a good diagnostic accuracy for the diagnosis of uterine cavity diseases. TVS had good specificity, but with low sensitivity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):533-538
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900006
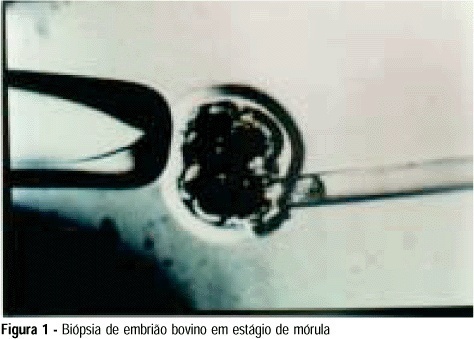
Purpose: to develop an animal model for the study of, and training in, bovine biopsies. Methods: cow ovaries were obtained from a slaughterhouse and transported to the laboratory where the oocytes were aspirated, maturated and submitted to in vitro fertilization. On the 5th day after fertilization, the embryos were biopsied, with the zona pellucida being opened with a cutting blade fitted to the light microscope. One or two blastomeres were removed from the embryos and left in coculture for three additional days. After this time, embryo development was evaluated in comparison to a control group by morphological study and cell counts using specific staining for nuclei. Results: forty of the 57 biopsied embryos reached the blastocyst stage (70.2%) and hatching was observed in 11 (27.5%). Forty-two blastocysts were obtained in the control group (73.7%) and 11 of them hatched (26.2%). Cell counts showed no significant differences between groups. Conclusions: we conclude that the proposed protocol is technically feasible and supplies a good number of embryos because of the easy technique for obtaining bovine oocytes, thus representing a method that could be adopted for training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):554-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900009
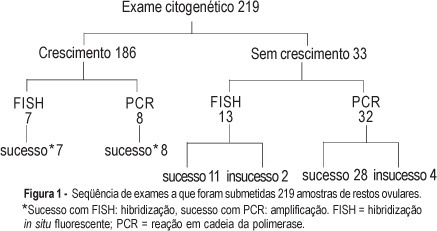
PURPOSE: to evaluate the performance of cytogenetic analysis, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the study of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination of spontaneous abortion material. METHODS: cytogenetic analysis was performed on 219 spontaneous abortion specimens. Forty of these cases were also submitted to fetal sex determination using nested-PCR. Thirty-two of these cases were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other eight were selected randomly. Twenty samples were submitted to the FISH technique, using probes for chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y. Thirteen of these samples were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other seven were randomly selected. The success rates of each technique were compared using the chi2 test and an established p<0.05 level of significance. The results of samples submitted to more than one test were evaluated for accuracy, using the cytogenetic result as the gold standard. RESULTS: cytogenetic analysis was successful in 84.9% of the samples and in 51.1% of them the results were abnormal: 65.2% trisomy, 17.9% triploidy, 9.4% tetraploidy, 4.2% chromosome X monosomy, and 1.1% each for double trisomy, tetrasomy and structural abnormality. The most frequent trisomy was that of chromosome 16 (39%). The success rate of FISH and PCR techniques (90%) did nod differ significantly from the cytogenetic analysis. In all cases submitted to more than one test, the results were identical to those obtained through cytogenetic analysis. Samples that failed to grow on cytogenetic test and that were submitted to other techniques of molecular biology had a success rate of 87.5 and 84.6% for PCR and FISH, respectively. CONCLUSION: cytogenetic analysis of spontaneous abortions had a high success rate and chromosomal anomalies were identified in over half of the cases. Molecular biology techniques (PCR and FISH) complemented the cytogenetic study and proved to be reliable in the detection of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):573-578
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200002
PURPOSE: to establish reference values for the length and area of the fetal corpus callosum between the 20th and 33rd weeks of gestation using three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS). METHODS: this cross-sectional study involved 70 normal pregnancies with gestational age between 20 and 33 weeks. An Accuvix XQ instrument with a convex volumetric transducer (3 to 5 MHz) was used. To assess the corpus callosum, a transfrontal plane was obtained using the metopic suture as an acoustic window. Length was obtained by measuring the distance between the proximal and distal extremities of the corpus callosum. Area was obtained by manual tracing of the external corpus callosum surface. The means, medians, standard deviations, and maximum and minimum values were calculated for the corpus callosum length and area. Scatter graphs were created to analyze the correlation between corpus callosum length and area and gestational age and biparietal diameter, the quality adjustments was verified according to the determination coefficient (R²). The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to assess the intraobserver variability. RESULTS: mean corpus callosum length increased from 21.7 (18.6 - 25.2 mm) to 38.7 mm (32.6 - 43.3 mm) between 20 and 33 weeks of pregnancy, respectively. Mean corpus callosum area increased from 55.2 (41.0 - 80.0 mm²) to 142.2 mm² (114.0 - 160.0 mm²), between 20 to 33 weeks of pregnancy, respectively. There was a strong correlation between corpus callosum length and area and gestational age (R² = 0.7 and 0.7, respectively) and biparietal diameter (R² = 0.7 and 0.6, respectively). Intraobserver variability was appropriate, with an ICC of 0.9 and 0.9 for length and area, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: reference values for corpus callosum length and area were established for fetuses between 20 and 33 weeks gestation. Intraobserver variability was appropriate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):621-629
The present study aims to determine if the use of cervical pessary plus progesterone in short-cervix (≤ 25 mm) dichorionic-diamniotic (DC-DA) twin pregnancies is equivalent to the rate of preterm births (PBs) with no intervention in unselected DC-DA twin pregnancies.
A historical cohort study was performed between 2010 and 2018, including a total of 57 pregnant women with DC-DA twin pregnancies. The women admitted from 2010 to 2012 (n = 32) received no treatment, and were not selected by cervical length (Non-Treated group, NTG), whereas those admitted from 2013 to 2018 (n = 25), were routinely submitted to cervical pessary plus progesterone after the diagnosis of short cervix from the 18th to the 27th weeks of gestation (Pessary-Progesterone group, PPG). The primary outcome analyzed was the rate of PBs before 34 weeks.
There were no statistical differences between the NTG and the PPG regarding PB < 34 weeks (18.8%; versus 40.0%; respectively; p = 0.07) and the mean birthweight of the smallest twin (2,037 ± 425 g versus 2,195 ± 665 g; p = 0.327). The Kaplan-Meyer Survival analysis was performed, and there were no differences between the groups before 31.5 weeks. Logistic regression showed that a previous PB (< 37 weeks) presented an odds ratio (OR) of 15.951 (95%; confidence interval [95%;CI]: 1.294-196.557; p = 0.031*) for PB < 34 weeks in the PPG.
In DC-DA twin pregnancies with a short cervix, (which means a higher risk of PB), the treatment with cervical pessary plus progesterone could be considered equivalent in several aspects related to PB in the NTG, despite the big difference between these groups.