Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):77-82
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200003
Purpose: to evaluate the nonpharmacologic treatment (reassurance) as a first line therapy for women with cyclical mastalgia, and to observe if a prolonged course of pain alters the outcome. Methods: we conducted a noncontrolled experimental study with a sample of 128 eligible women with a clear history of cyclical mastalgia treated with reassurance. A visual linear analogical scale of the pain was used before and after treatment in order to assess its severity and the mastalgias were classified into degrees I (mild), II (moderate) and III (severe) according to the intensity of pain. We also used a modified Cardiff Breast Score (CBS) to assess the clinical response. The data analysis was performed using the chi² test (Epi-Info 6.04 software). Results: we verified a success rate of 59.4% with reassurance, but there was no significant statistical difference between the groups (p = 0.16) with different degrees of mastalgia. The less satisfactory response to the nonpharmacologic treatment in those pacients with a prolonged course of pain was only apparent, since there was no significant statistical difference (p = 0.14). Conclusion: reassurance should be always tried as the first choice treatment for women with cyclical mastalgia, independently of pain intensity. Prolonged course of pain did not alter the outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):771-775
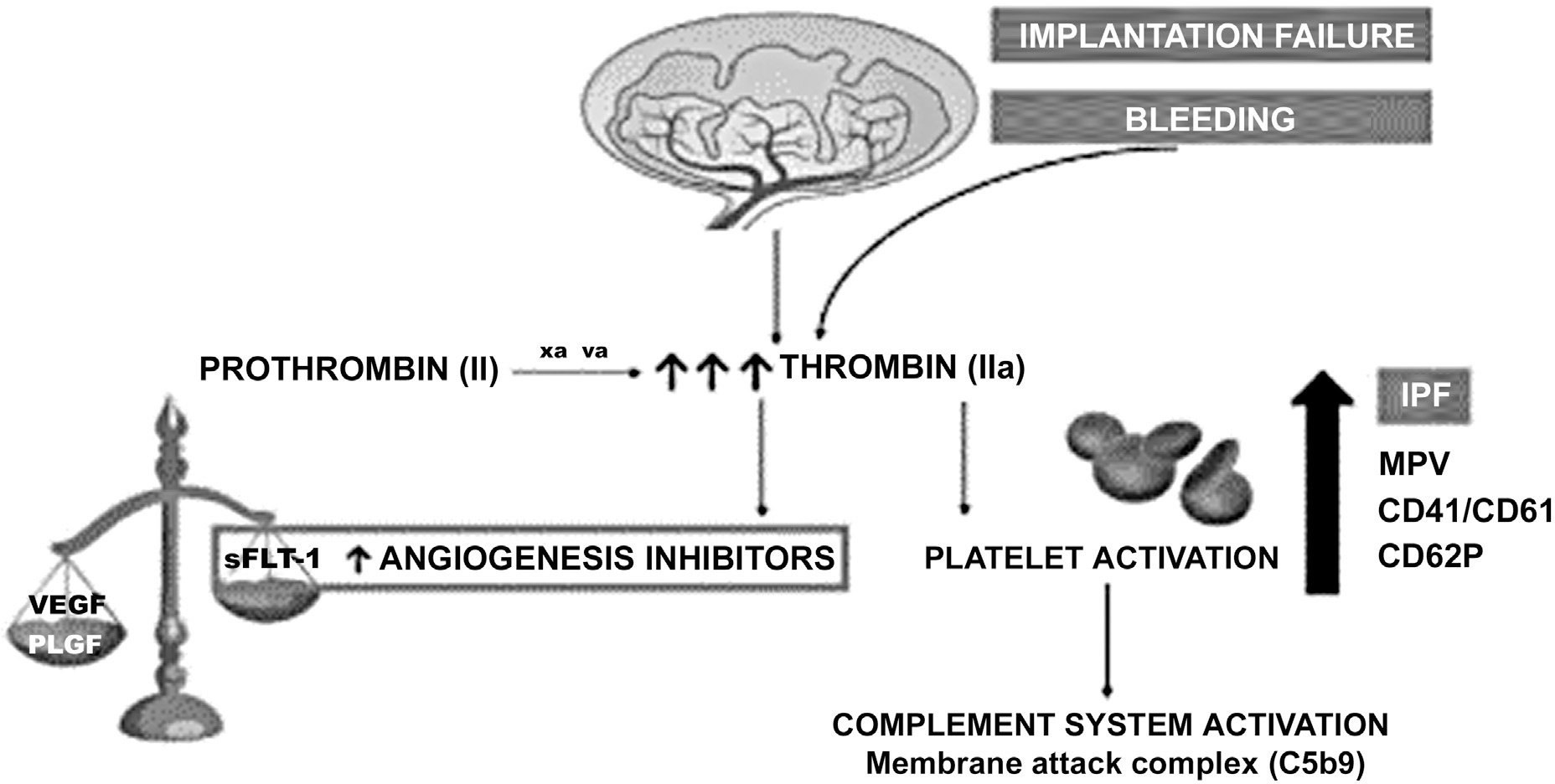
Preeclampsia, a human pregnancy syndrome, is characterized by elevated blood pressure and proteinuria after the 20th week of gestation. Its etiology remains unknown, and its pathophysiological mechanisms are related to placental hypoperfusion, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and coagulation cascade activation. Recently, the role of the complement system has been considered. This syndrome is one of the main causes of maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity. This article discusses the hypothesis of preeclampsia being triggered by the occurrence of inadequate implantation of the syncytiotrophoblast, associated with bleeding during the first stage of pregnancy and with augmented thrombin generation. Thrombin activates platelets, increasing the release of antiangiogenic factors and activating the complement system, inducing the membrane attack complex (C5b9). Immature platelet fraction and thrombin generation may be possible blood biomarkers to help the early diagnosis of preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):771-778
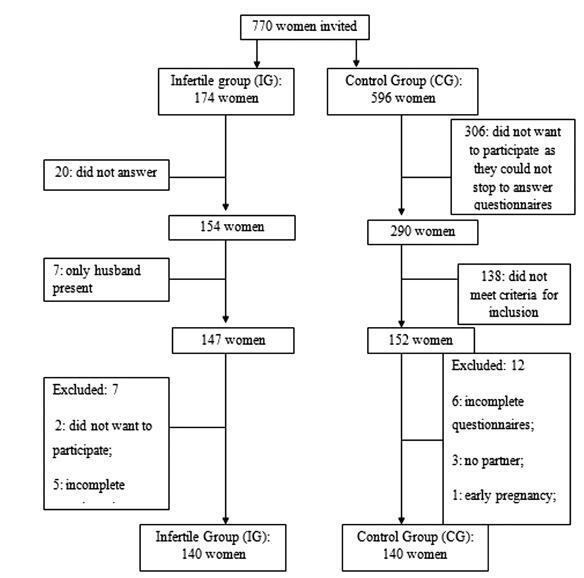
To assess the sexual function, anxiety, and depression of infertile women relative to a control group.
Infertile women (infertile group, IG) of reproductive age were invited to participate in this controlled study. A control group (CG) of women was recruited from the general population of the same city. Sexual function was assessed by the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and anxiety and depression were measured by the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS).
A total of 280 women participated in the present study, 140 in the IG and 140 in the CG. The analysis of the FSFI scores showed that 47 women (33.57%) in the IG and 49 women (35%) in the CG had sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.55; p = 0.90). Women with anxiety or depression had a greater risk of sexual dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction increased the risk of anxiety and depression. Married women had a lower risk of depression than single women who were living with their partners.
Infertilewomenhadno increased riskof sexual dysfunction relativetocontrols. Anxiety and depression increased the risk of sexual dysfunction in the studied population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):772-773
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is an obstetric disease with a multifactorial cause that affects ∼ 5% of pregnant women. Vision can be affected with varying severity, and retinal detachment is a very rare complication. It tends to be bilateral, diagnosed postpartum, and more prevalent in women who are primiparous and/or undergo caesarean delivery. The condition typically resolves completely and rarely causes total visual loss in the affected women. Fluorescence angiographic findings support the hypothesis that retinal detachment in PE is secondary to choroidal ischemia from intense arteriolar vasospasm. The present article is related to a case of a 37-year-old pregnant woman who had PE associated with a progressive blurred vision, diagnosed by ophthalmology as serous macular detachment of the retina.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):773-780
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004001000004
PURPOSE: to compare the information obtained with pelvic and transvaginal ultrasonography (USG), hystero-salpingography (HSG), diagnostic hysteroscopy (HSC), pelvic nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (PNMR), three-dimensional hysterosonography (3D HSSNG), to optimize and simplify the investigation about cervical and corporeal uterine factors in conjugal infertility. METHODS: in the period between January and July 2003, fifty women reporting infertility for at least two years were submitted to USG, HSG, HSC, PNMR, and 3D HSSNG as tracking examinations for uterine factor diagnosis. The endocervical canal, as well as the endometrium, myometrium, and the presence of uterine malformations were investigated. The results of each examination were analyzed and compared. RESULTS: of the 50 women studied, 12 (24%) presented alteration in at least one of the examinations. When 3D HSSNG was compared to USG, 3D HSSNG provided additional information in 7 cases (58.3%); when compared to HSG, it provided additional information in 7 cases (58.3%); when compared to HSC, it provided additional information in 4 cases (32.1%), and when compared to PNMR, it provided additional information in 6 cases (50%). There were only two cases in which HSG detected alterations of the endocervical canal that were not visualized using 3D HSSNG. In the other cases 3D HSSNG imparted the same diagnosis; furthermore, it provided additional information in comparison to the other examinations. Statistical analysis using the kappa test demonstrated that the diagnoses obtained by 3D HSSNG were in agreement with those obtained with USG, HSG and PNMR (p<0,05). When the HSG and 3D HSSNG results were combined, all conditions associated with infertility could be precisely diagnosed, using only these examinations. CONCLUSION: the association of the HSG with 3D HSSNG may be sufficient for the diagnosis of cervical and corporeal uterine factors in infertility, reducing the number of examinations for each patient, the total cost, as well as the anxiety and the delay in treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):774-775
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):775-779
To calculate and analyze the mortality rates from breast cancer in women under 50 years of age in Colombia and to compare them with those of other countries in the region.
Based on data from the registry of deaths in 2018 and the results of the National Population and Housing Census of Colombia for the same year, specific mortality rates in women with breast cancer, specific mortality according to age group, standardized by age, proportional mortality, potential years of life lost, and years of life expectancy lost in women under 50 years of age who died from breast cancer were calculated. The mortality rate of regional countries was consulted on the Global Cancer Observatory webpage.
In the group from 20 to 49 years, the specific mortality rate was higher in the age range from 45 to 49 years, with a rate of 23.42 × 100,000, a value that was above the specific mortality rate due to breast cancer in women in Colombia, 15.17 × 100.000. In the age range of 45 to 49 years, the potential years of life lost were 42.16. Of the 0.275 years of life expectancy lost by the population due to this neoplasia, women under 50 years of age represented 0.091 (33%). Colombia is the fifth in the rank of mortality in Latin American countries in this age group.
Breast cancer in patients from 30 to 59 years is the number one cause for the decrease in life expectancy of women in Colombia. Women under 50 years of age represent one third of this decrease. This neoplasm is also the leading cause of mortality in women younger than 50 years in South America.