Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):754-763
The serum ischemia modified albumin (IMA), biglycan, and decorin levels of pregnant women who were hospitalized for threatened preterm labor were measured.
Fifty-one consecutive pregnant women with a single pregnancy between the 24th and 36th weeks with a diagnosis of threatened preterm labor were included in the present prospective cohort study.
As a result of multivariate logistic regression analysis for predicting preterm delivery within 24 hours, 48 hours, 7 days, 14 days, ≤ 35 gestational weeks, and ≤ 37 gestational weeks after admission, area under the curve (AUC) (95% confidence interval [CI[) values were 0.95 (0.89–1.00), 0.93 (0.86–0.99), 0.91 (0.83–0.98), 0.92 (0.85–0.99), 0.82 (0.69–0.96), and 0.89 (0.80–0.98), respectively. In the present study, IMA and biglycan levels were found to be higher and decorin levels lower in women admitted to the hospital with threatened preterm labor and who gave preterm birth within 48 hours compared with those who gave birth after 48 hours.
In pregnant women admitted to the hospital with threatened preterm labor, the prediction preterm delivery of the combined model created by adding IMA, decorin, and biglycan in addition to the TVS CL measurement was higher than the TVS CL measurement alone.
The present trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT04451928.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):755-760
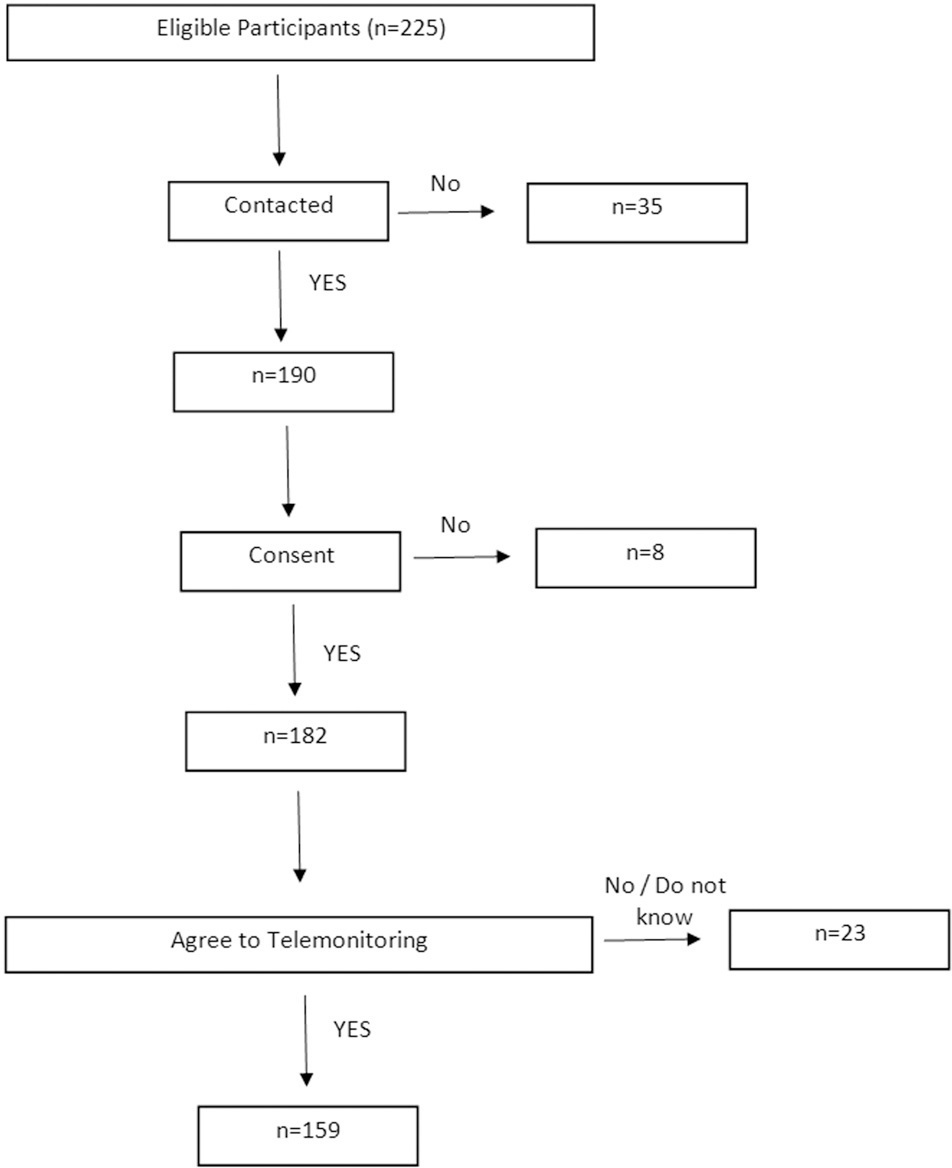
To evaluate the acceptance of telemedicine and determine its associated factors in an urogynecology outpatient clinic of a public hospital in Brazil.
The present was a cross-sectional study performed between June and November 2020. The included patients had their elective appointments postponed due to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The variables considered regarding the acceptance of telemedicine were: urogynecologic diagnosis, age, level of schooling, place of residence, access to the internet, type of device used, frequency of internet use, and use of social media platforms. The categorical variables were described by their absolute and relative frequencies. The association among variables was evaluated through the Fisher exact test, and univariate and multivariate analyses, considering the acceptance of telemedicine as the dependent variable.
A total of 225 patients were listed, and 182 agreed to participate. The mean age was 59 years old, 81.3% of the patients had access to the internet, and 87.3% of them accepted telemedicine. There were statistically significant associations regarding the acceptance of telemedicine and high levels of schooling (p< 0.01), internet access (p< 0.01), daily use of the internet (p< 0.01), access through personal mobile phone (p< 0.01), and access through the participant's own residence (p< 0.01). In the univariate and multivariate analyses, only high levels of schooling were associated with the acceptance of telemedicine (Adjusted odds ratio: 4.82; 95% confidence interval = 1.59–14.65).
Most of the urogynecology patients of a public hospital in a developing country accepted telemedicine. Internet access and level of schooling were the factors associated with the acceptance of telemedicine in urogynecology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):755-755
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):757-762
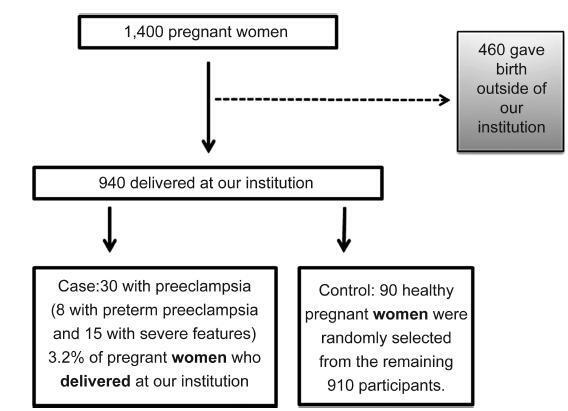
To evaluate whether the circulating level of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase- 4 (TIMP-4) in the period between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation is a predictor of preeclampsia.
We have performed a case-control study, nested in a prospective study cohort in Ribeirão Preto, in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Of the 1,400 pregnant women evaluated between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation, 460 delivered in hospitals outside of our institution. Of the 940 pregnant women who completed the protocol, 30 developed preeclampsia. Healthy pregnant women (controls, n = 90) were randomly selected from the remaining 910 participants. From blood samples collected between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation, we performed a screening of 55 angiogenesis-related proteins in 4 cases and 4 controls. The protein TIMP-4 was the most differentially expressed between cases and controls. Therefore, wemeasured this protein in all cases (n = 30) and controls selected (n = 90).
There were no differences in the plasma TIMP-4 levels of cases compared with controls (1,144 263 versus 1,160 362 pg/mL, respectively; p > 0.05).
Plasma TIMP-4 levels were not altered at 20 to 25 weeks of gestation, before the manifestation of clinical symptoms; therefore, they are not good predictors of the development of preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):759-768
To analyze the long-term effects of antineoplastic treatments on patient fertility.
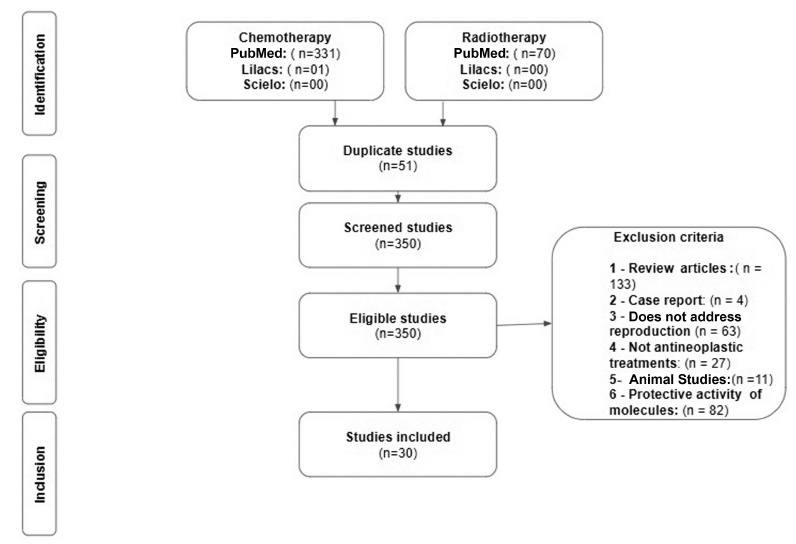
The studies were selected through the New PubMed, Scielo and Lilacs databases along with references used for the creation of the present work. For the selection of studies, articles published between the periods from January 1, 2015 to April 6, 2020 in the English, Portuguese and Spanish languages were used. As inclusion criteria: cohort studies and studies conducted in vitro. As exclusion criteria: review articles, reported cases, studies that do not address thematic reproduction, studies that do not address the cancer theme, articles that used animals, articles that address the preservation of fertility and articles in duplicate in the bases.
The collected data included: age of the patient at the beginning of treatment, type of neoplasm, type of antineoplastic treatment, chemotherapy used, radiotherapy dosage, radiotherapy site, effect of antineoplastic agents on fertility and number of patients in the study.
Thirty studies were evaluated, antineoplastic chemotherapy agents and radiotherapy modulate serum hormone levels, reduces germ cell quantities and correlated with an increase in sterility rates. The effects mentioned occur in patients in the prepubertal and postpubertal age.
Antineoplastic treatments have cytotoxic effects on the germ cells leading to hormonal modulation, and pubertal status does not interfere with the cytotoxic action of therapies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):759-767
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200009
PURPOSE: to carry out a literature review to evaluate the impact of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) on maternal and perinatal morbidity. METHODS: specialized data bases such as SCI and MEDLINE were used to identify studies related to the terms: "in vitro fertilization", "assisted reproduction" and "reproductive techniques" in combination with "morbidity", "maternal mortality", "perinatal mortality", and "neonatal mortality". RESULTS: data from published studies allow us to conclude that maternal morbidity is related to an increase in the number of multiple pregnancies. In addition, some studies have reported an increased incidence of pregnancy-induced hypertension and gestational diabetes. Specialized multidisciplinary prenatal care has been recommended to obtain optimal results. An increase in the number of multiple pregnancies considerably increases maternal, fetal and neonatal complications. There is also evidence of an increase in congenital malformations. The particular characteristics of this group of women and the different techniques of assisted reproduction, particularly ICSI, in the etiology of congenital defects were discussed, but no clear differences have been established between the various procedures. Some recent metanalyses show that the number of fetal malformations in infants born as a result of ICSI is greater than in spontaneously conceived infants, but not more frequent than in those born as a result of other ART. There is no consensus regarding whether this fact is a result of the procedure itself, of manipulation of the gametes, ovulation induction, if it is due to the fact that these couples are infertile or a result of the time they take to become pregnant. Few studies have carried out a prolonged, consistent and systematic evaluation of the perinatal evolution of infants born following the use of frozen embryos. CONCLUSIONS: with respect to fetal malformations, there is definitely a higher incidence rate among infants born as a result of ART compared to those conceived naturally (RR: 1.4-2.0; 95% CI: 1.3-2.7). Insufficient time and data do not yet permit analysis of the outcome of pregnancies resulting from the use of frozen embryos. It is not clear whether these findings are due to the characteristics of the couples who are submitted to these procedures or to the peculiarities of each method. Many of the problems related to maternal and perinatal morbidity are due to the significant number of multiple pregnancies originating from ART. More studies are required in order to clarify these aspects of human reproduction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):759-764
Breast surgery is considered a clean surgery; however, the rates of infection range between 3 and 15%. The objective of the present study was to intraoperatively investigate the presence of autochthonous microbiota in the breast.
Pieces of breast tissue collected from 49 patients who underwent elective breast surgery (reconstructive, diagnostic, or oncologic) were cultured. The pieces of breast tissue were approximately 1 cm in diameter and were removed from the retroareolar area, medial quadrant, and lateral quadrant. Each piece of tissue was incubated in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth for 7 days at 37°C, and in cases in which the medium became turbid due to microorganism growth, the samples were placed in Petri dishes for culturing and isolating strains and for identifying species using an automated counter.
Microorganism growth was observed in the samples of 10 of the 49 patients (20.4%) and in 11 of the 218 pieces of tissue (5%). The detected species were Staphylococcus lugdunensis, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Sphingomonas paucimobilis, and Aeromonas salmonicida. No patient with positive samples had clinical infection postoperatively.
The presence of these bacteria in breast tissue in approximately 20% of the patients in this series suggests that breast surgery should be considered a potential source of contamination that may have implications for adverse reactions to breast implants and should be studied in the near future for their oncological implications in breast implant-associated large-cell lymphoma etiology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):76-83
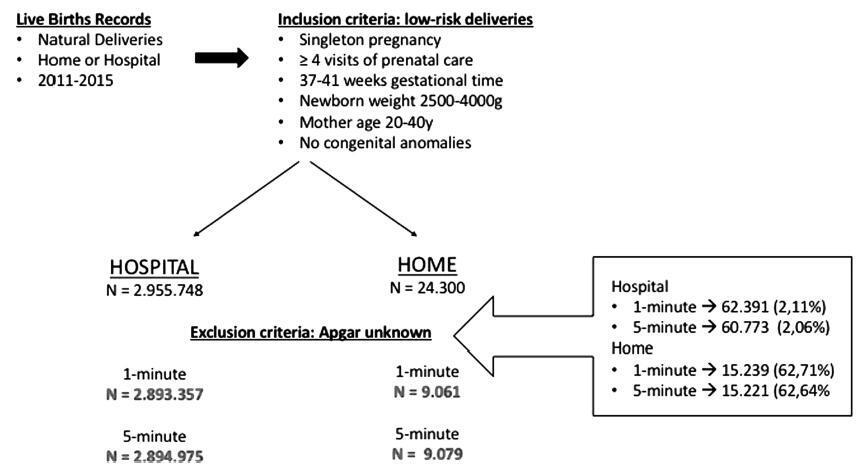
To promote informed choice for women and to compare home andhospital births in relation to the Apgar score.
Mother’s profile and Apgar score of naturally born infants (without forceps assistance) in Brazil between 2011 and 2015, in both settings-hospital or home-were collected from live birth records provided by the Informatics Department of the Unified Health System (DATASUS, in the Portuguese acronym). For the analysis, were included only data fromlow-riskdeliveries, including gestational time between 37 and 41weeks, singleton pregnancy, at least four visits of prenatal care, infants weighing between 2,500 g, and 4,000 g, mother age between 20-40 years old, and absence of congenital anomalies.
Home birth infants presented significantly higher risk of 0-5 Apgar scores, both in 1 minute (6.4% versus 3%, odds ratio [OR] = 2.2, confidence interval [CI] IC 2-2.4) and in 5 minutes (4.8% versus0.4%,OR = 11.5,CI 10.5-12.7). Another findingis related to recovery estimateswhen from an initially bad 1-minute Apgar (<6) to a subsequently better 5-minute Apgar (> 6). In this scenario, home infants had poorer recovery, Apgar scorewas persistently < 6 throughout the fifth minute in most cases (71% versus 10.7%, OR 20.4, CI 17-24.6).
The results show worse Apgar scores for babies born at home, compared with those born at the hospital setting. This is a pioneer and preliminary study that brings attention concerning differences in Apgar score related to home versus hospital place of birth in Brazil.