Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):74-80
To evaluate the impact of the presence of criteria for severe maternal morbidity and maternal near miss associated with hypertensive disorders on maternal and perinatal outcomes in a maternity school.
The present is a sub-analysis of a larger study involving 27 centers in Brazil that estimated the prevalence of serious maternal morbidity and near miss. It is an analytical and cross-sectional study with a quantitative approach, involving 928 women who were cared for at Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand (MEAC, in Portuguese), Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC, in Portuguese), from July 2009 to June 2010. The women were diagnosed with near miss according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. The sample was divided into 2 groups: patients with (n = 827) and without hypertension (n = 101). The results were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05. The Pearson chi-squared and Fisher Exact tests were used for the categorical variables, and the Mann–Whitney U test was used for the continuous variables.
In total, 51 participants with maternal near miss criteria were identified, and 36 of them had hypertensive disorders. Of these, 5 died and were obviously excluded from the near miss final group. In contrast, we observed 867 cases with non-near miss maternal morbidity criteria. During this period, there were 4,617 live births (LBs) in the institution that was studied.
In the severe morbidity/maternal near miss population, the presence of hypertensive complications was prevalent, constituting a risk factor for both the mother and the fetus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):74-79
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between women's menstrual experience and preferred changes in their menstrual cycles. METHODS: a cross-sectional study design was used. A total of 420 women were interviewed. Participants complied with the following criteria: age (18 to 20, 25 to 34 and 45 to 49 years); schooling (<8 years and >12 years); having menstruated during the three months previous to the study. Subjects were selected in the city of Campinas (SP), in nine private and seven public health services. For data collection, a questionnaire was prepared on the basis of the results of a previous pilot study that consisted of small groups. A data bank was prepared with the information registered in the questionnaires and the analysis was carried out with SAS, version 8.2. For the statistical analysis, the Pearson chi2 test and the Fisher exact test were used to evaluate the association between variables (p<0.05). RESULTS: most subjects preferred greater than once a month intervals between menstruations. There was an association of the typical menstrual intervals experienced by women (p=0.0248) and the degree of interference of menstruation with daily activities (p=0.048) with the preferred interval between menses. However, there was no association between preferred intervals by women and the following characteristics of pain: duration, intensity and use of medication. CONCLUSIONS: the results suggest that women would like intervals longer than one month or to never menstruate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(2):74-79
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000200006
PURPOSE: To analyze the prevalence of insulin resistance, according to different biochemical and anthropometric measurements in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. METHODS: A total of 189 patients with polycystic ovary syndrome were retrospectively analyzed. Insulin resistance diagnosis was performed using fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, QUICKI, insulin sensibility index and glucose/fasting insulin ratio. Body mass index and lipid accumulation product were used. Data were analyzed statistically by descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Tukey post-test, and Pearson's correlation. RESULTS: The polycystic ovary syndrome patients had a mean age of 24.9±5.2 and a mean body mass index of 31.8±7.6. The percentage of obese patients was 57.14%. Among the methods of insulin resistance investigation, the insulin sensibility index was the technique that most detected (56.4%) the presence of insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. The insulin resistance was detected in 87% of obese patients. The fasting glucose/fasting insulin ratio and insulin sensibility index were strongly correlated with lipid accumulation product. CONCLUSION: The prevalence of insulin resistance varied according to the method used, and it was greater the higher the body mass index. Lipid accumulation product was also related to insulin resistance.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):740-745
To assess the possible impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth in 2020 in relation of the last 10 years.
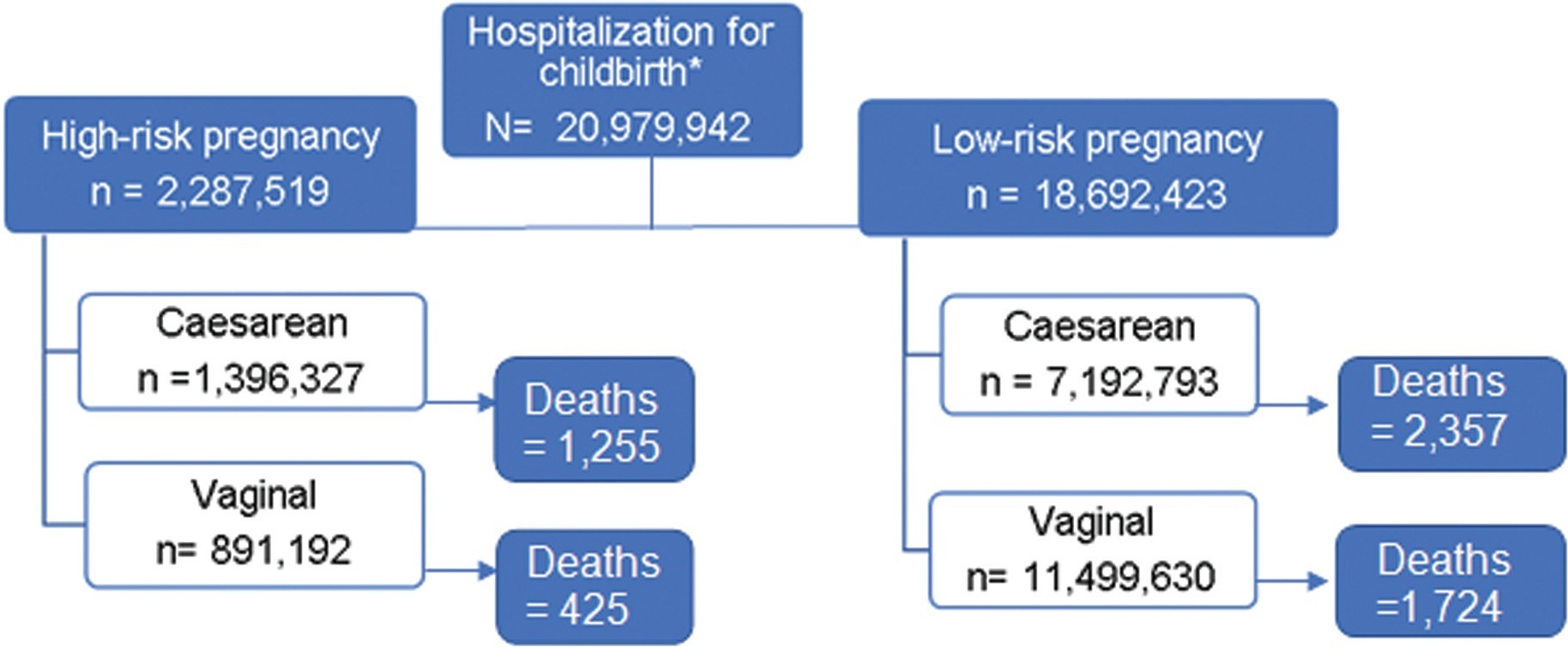
An ecological study with pregnant women who underwent hospital births at the Brazilian unified public health service (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym) in Brazil from 2010 to 2020. The mortality among admissions for childbirth was obtained based on the number of admissions for childbirth with reported death as outcome divided by the total number of admissions. The underlying gestational risk and route of delivery were considered based on the national surveillance system. The average mortality for the period between 2010 and 2019 (baseline) was compared with the rate of deaths in 2020 (1st pandemic year); the rate ratio was interpreted as the risk of death in 2020 in relation to the average of the previous period (RR), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
In 2020, the 1st year of the COVID-19 pandemic, 1,821,775 pregnant women were hospitalized for childbirth and 651 deaths were reported, which represents 8.7% of the total hospitalizations and 11.3% of maternal deaths between 2010 and 2020. There was an increase in maternal mortality after births in 2020 compared with the average for the period between 2010 and 2019, specially in low-risk pregnancies, both in vaginal (RR = 1.60; 95%CI:1.39–1.85) and cesarean births (RR = 1.18; 95%CI:1.04–1.34).
Maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth according to SUS data increased in 2020 compared with the average between 2010 and 2019, with an increment of 40% in low-risk pregnancies. The increase was of 18% after cesarean section and of 60% after vaginal delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):740-748
To analyze if umbilical artery pH (pHua) ≤7.00 and umbilical artery blood deficit (BDua) ≥12.00 mmol/L are good predictors of adverse neonatal outcomes.
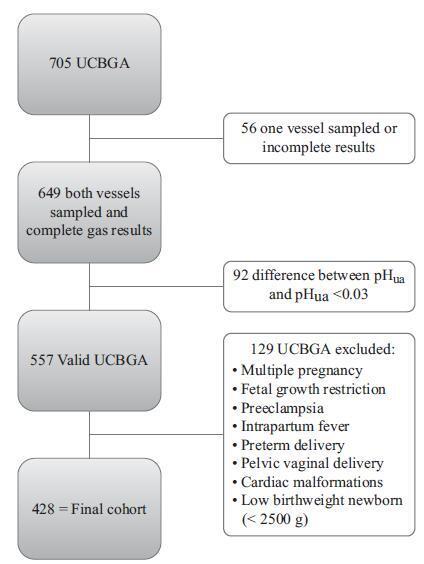
This was an observational, longitudinal and retrospective cohort study, conducted at the department of obstetrics and gynecology of Centro Hospitalar Tondela Viseu between September 2013 and September 2015. Total cohort and subgroup analysis were performed: group A-women with umbilical cord blood gas analysis (UCBGA) performed for non-reassuring fetal cardiotocographic patterns, placental abruption, or shoulder dystocia; and group B-all the others. Assays were made with the software SPSS for Windows, Versions 20.0 and 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
A total of 428 UCBGAs met the inclusion criteria. The group analysis revealed an association between group A and pHua ≤7.00, as well as between BDua ≥12.00 mmol/L and 1st minute Apgar score ≤4 (p = 0.011). After the application of the logistic regression models in the total cohort analysis, pHua ≤7.00 had an impact in the occurrence of acute neonatal hypoxia (odds ratio [OR]: 6.71; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.21-37.06; p = 0.029); multiparous women had a higher risk of delivering a newborn with first minute Apgar score ≤4 and acute neonatal hypoxia (OR: 5.38; 95% CI: 1.35-21.43; p = 0.017; and OR: 2.66; 95% CI: 1.03-6.89, p = 0.043, respectively); women who had urologic problems during pregnancy had a higher risk of delivering a newborn with 5th minute Apgar score ≤7 (OR: 15.17; 95% CI: 1.29-177.99; p = 0.030); and shoulder dystocia represented a 15 times higher risk of acute neonatal hypoxia (OR: 14.82; 95% CI: 2.20-99.60; p = 0.006).
The pHua and the BDua are predictors of adverse neonatal outcome, and UCBGA is a useful tool for screening newborns at risk. Universal UCBGA should be considered for all deliveries, as it is an accurate screening test for neonatal hypoxia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):741-743
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900011
Ectopic pregnancy is the implantation and development of the ovum outside the uterine cavity; it needs a quick diagnosis and an urgent treatment. The presence of the corpus luteum in the ovary that is contralateral to the ectopic pregnancy is presumptive evidence for ovum transmigration, which may be the cause of ectopic pregnancy. In 1994, a multinational clinical trial proved the superiority of levonorgestrel over the existing emergency contraceptive products. In the present study, we describe the case of a 27-year-old woman with ectopic pregnancy and a contralateral corpus luteum after use of hormonal emergency contraception (levonorgestrel), because of failure of the used contraception method (condom). The patient was treated with laparoscopic surgery that was successful.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):741-741
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):741-741