Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):735-739
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900010
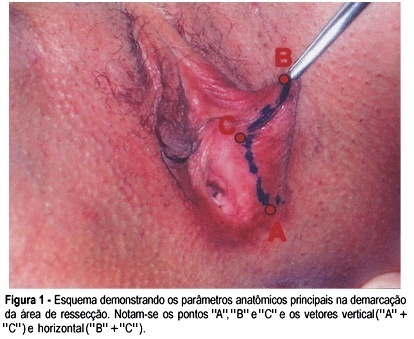
PURPOSE: to describe the use of a superior labial flap for the treatment of labia minora hypertrophy. METHODS: from May, 1998 to July, 2002 10 patients with labia minora hypertrophy were submitted to reduction of the labial excess through the resection of the inferior segment by an L-shaped incision. The transversal incision was done starting on the labial external border towards the hymenal caruncles, and the longitudinal incision, from that point until near the furcula. The border of the superior flap was then lowered to eliminate the defect caused by the inferior resection. RESULTS: within an average period of 45 days after surgery, the patients were satisfied with its esthetical and functional aspects. The local sensibility did not change. Only two cases presented complications: one case with perineal ecchymosis and the other with partial, early unilateral dehiscense. Infection, necrosis and late dehiscense were not observed. CONCLUSION: the utilization of the superior flap in the correction of labia minora hypertrophy produces a satisfactory esthetical and functional result with few complications and easy resolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):736-742
Thyroid diseases are the second most common endocrine disorders in the reproductive period of women. They can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, low Apgar score, low birthweight (LBW) or fetal death. The aim of the present study is to explore thyroid dysfunction and its relationship with some poor perinatal outcomes (Apgar Score, low birthweight, and preterm delivery).
Dried blood spot samples from 358 healthy pregnant women were analyzed for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), total thyroxine (TT4), and thyroglobulin (Tg). Neonatal data were collected upon delivery. Four groups were formed based on thyroid function tests (TFTs).
Of the 358 tested women, 218 (60.72%) were euthyroid. Isolated hypo thyroxinemia was present in 132 women (36.76%), subclinical hyperthyroidism in 7 women (1.94%), and overt hypothyroidism in 1 (0.28%). The perinatal outcomes IUGR (p = 0.028) and Apgar score 1 minute (p = 0.015) were significantly different between thyroid function test [TFT]-distinct groups. In the multiple regression analysis, TT4 showed a statistically significant inverse predictive impact on LBW (p < 0.0001), but a positive impact of Tg on LBW (p = 0.0351).
Thyroid hormones alone do not have a direct impact on neonatal outcomes, but the percentage of their participation in the total process cannot be neglected. Based on the regression analysis, we can conclude that TT4 and Tg can be used as predictors of neonatal outcome, expressed through birthweight and Apgar score. The present study aims to contribute to determine whether a test for thyroid status should become routine screening during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):737-743
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of anxiety and depression in main caretakers of patients with terminal breast or gynecological cancer. METHODS: for this cross-sectional study, 133 informal caretakers of terminally-ill breast and gynecologic cancer patients were included. Patients were hospitalized for palliative care in the Oncology Clinic of the "Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher (Campinas, Brasil) from August 2002 to May 2004. Seventy-one of the patients had breast cancer and 62 had gynecological malignancies. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HAD) was applied to these informal caretakers, in order to detect anxiety and depression, and they were also interviewed to provide additional information regarding their age, gender, religion, relation to patient, current occupation, if they cared for other people, whether their routine had changed and whether other people helped them to care for the patient. Logistic regression was used to calculate the odds ratio (OR) and its confidence interval (CI), used to assess the relationship between the diagnoses of anxiety and depression among the informal caretakers. For multiple analyses, the stepwise criterion for variable selection was used. RESULTS: 43% percent of the patients identified their daughters as their main caretaker, and 24%, their husbands. Most of the caretakers were over 35 years old (63%), 68% were female, 59% were unemployed, 47% cared for another person and 84% referred that his/her routine had changed because of caring. Anxiety was detected in 99 caretakers (74.4%) and depression in 71 (53.4%). Anxiety and depression were strongly correlated (odds ratio 5.6; 95% confidence interval 2.2 to 15.9). Bivariate analysis disclosed that the patients' husbands were less affected by depression, but multivariate analysis revealed that only the fact of being male was related to a lower prevalence of anxiety. CONCLUSION: caring for terminally-ill cancer patients led to high prevalence of anxiety and depression. Only men and the patients' husbands were found to have a lower prevalence of anxiety.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):737-739
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):739-745
To evaluate factors associated with anxiety and the effect of simulation-based training (SBT) on student anxiety, self-confidence and learning satisfaction in relation to pelvic and breast examination.
A longitudinal study was conducted with 4th year medical students at the Universidade José do Rosário Vellano. A 12-item, self-report questionnaire on student anxiety at performing gynecological examinations was applied before and after SBT, with answers being given on a Likert-type scale. After training, the self-confidence levels and satisfaction of the students related to the learning process were also evaluated.
Eighty students with a mean age of 24.1 ± 4.2 years were included in the study. Of these, 62.5% were women. Pre-SBT evaluation showed that students were more anxious at performing a pelvic examination than a breast examination (2.4 ± 1.0 versus 1.7 ± 0.8, respectively; p < 0.001). The primary reason for anxiety regarding both pelvic and breast examination was fear of hurting the patient. SBT significantly reduced student anxiety (2.0 ± 0.8 versus 1.5 ± 0.5, respectively; p < 0.001). The satisfaction and self-confidence of the students were found to be high (6.8 ± 0.3 and 6.0 ± 0.9, respectively), with no difference between genders.
The use of SBT in teaching students to perform pelvic and breast examinations resulted in reduced anxiety and increased self-confidence in a group of medical students of both genders, with high levels of satisfaction in relation to the training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(10):739-744
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003001000007
PURPOSE: to verify the contribution of maternal age, parity, twin pregnancy, hypertensive syndrome, and premature rupture of membranes as risk factors for cesarean section. METHODS: after approval by the Ethics in Research Committee of the "Maternidade Professor Monteiro de Morais" - Recife, PE - Brazil, for a case control study, the authors analyzed data from 3919 pregnant women, without two or more prior cesarean sections, who gave birth to alive newborns with gestational age equal to or more than 28 weeks, weighing at least 1,000 g, on cephalic presentation, from September 1, 1999 to August 31, 2000. The case group included women submitted to cesarean section and the control group included women submitted to vaginal delivery. With the data collected from obstetric and neonatal reports, the authors performed multivariate analysis by logistic regression to determine a mathematical equation that associates cesarean probability due to more than one independent variable acting as risk factor, determining odds ratio with a confidence interval of 95% (95% CI), for the variables: maternal age, parity, twin pregnancy, hypertensive syndrome, and premature rupture of membranes. RESULTS: the chances for cesarean section significantly increased 8.3 times in twin pregnancy (OR = 8.3; 95% CI: 3.7-19.1), 3.4 in hypertensive syndrome (OR = 3.4; 95% CI: 2.9-4.0), 1.9 in primiparity (OR = 1.9; 95% CI: 1.8-2.0), 1.5 in maternal age over 34 years (OR = 1.5; 95% CI: 1.2-1.8), and 1.2 in the presence of premature rupture of membranes (OR = 1.2; 95 %CI: 1.0-1.4). CONCLUSIONS: the risk for cesarean section was greater in the presence of premature rupture of membranes, maternal age greater than 34 years, primiparity, hypertensive syndrome, and twin pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
To compare the perinatal outcomes of fetuses with isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia after fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion (FETO) and antenatal expectant management.
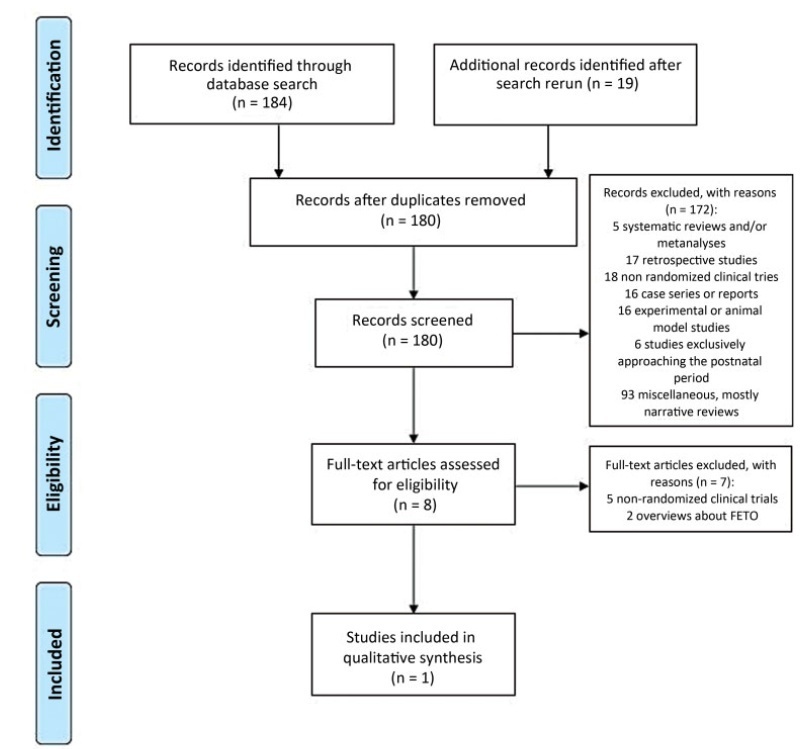
In this rapid review, searches were conducted in the MEDLINE, PMC, EMBASE and CENTRAL databases between August 10th and September 4th, 2020. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs or cluster-RCTs published in English in the past ten years were included.
We retrieved 203 publications; 180 studies were screened by abstract. Full-text selection was performed for eight studies, and 1 single center RCTmet the inclusion criteria (41 randomized women; 20 in the FETO group, and 21 in the control group).
Data collection was performed independently, by both authors, in two steps (title and abstract and full-text reading).
There were no cases of maternal mortality. The mean gestational age at delivery was of 35.6±2.4 weeks in the intervention group, and of 37.4±1.9 weeks among the controls (p<0.01). Survival until 6 months of age was reported in 50% of the intervention group, and in 5.8% of the controls (p<0.01; relative risk: 10.5; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.5-74.7). Severe postnatal pulmonary hypertension was found in 50% of the infants in the intervention group, and in 85.7% of controls (p=0.02; relative risk: 0.6; 95%CI: 0.4-0.9). An analysis of the study indicated some concerns of risk of bias. The quality of evidence was considered moderate to low.
Current evidence is limited but suggests that FETO may be an effective intervention to improve perinatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):74-79