Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):66-71
To investigate the association between the intensity of climacteric symptoms and sexual dysfunction in women aged 40 to 65 years.
Observational, analytic, cross-sectional study conducted with 63 women aged 40 to 65 treated at the gynecology outpatient clinic of a public hospital in northeastern Brazil. A questionnaire was used to collect identification data, clinical information, gynecological-obstetric data, lifestyle traits and information on chronic diseases. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were evaluated by means of the Blatt-Kupperman index and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) respectively. The association between the two indices was investigated using the chi-squared test; the difference in mean scores on the FSFI as a function of menopausal status was evaluated by Student's t-test. The significance level was set to p < 0.05.
The mean value of the Blatt-Kupperman index was 26.42 (standard deviation [SD]: 4.52); 36.51% of the women exhibited severe symptoms. The mean score on the FSFI was 21.84 (SD: 4.11). More than half of the analyzed women (58.73%) exhibited sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.5). Regarding the association between the Blatt- Kupperman index and the FSFI, the greater the intensity of the climacteric symptoms (Blatt-Kupperman), the higher the frequency of sexual dysfunction (FSFI). Sexual dysfunction was exhibited by 100% of the participants with severe climacteric symptoms, 70.59% of those with moderate symptoms, and only 9.09% with mild symptoms (p < 0.001).
The application of the Blatt-Kupperman index and of the FSFI allowed the detection of an association between the severity of climacteric symptoms and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
Summary
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):66-66
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):66-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200003
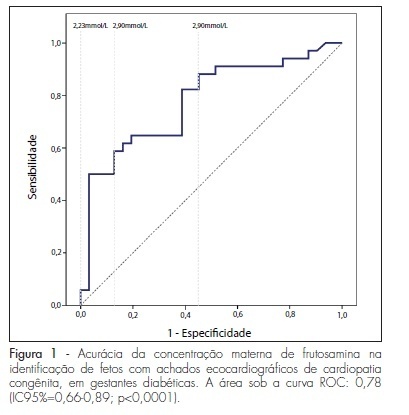
PURPOSE: to evaluate the importance of maternal plasma concentration of fructosamine as an indicator of fetal congenital cardiopathies in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. METHODS: this was a retrospective study conducted on 91 pregnant women with diabetes mellitus who underwent routine fetal echocardiography at a university reference center in fetal medicine. Sixty-five patientes who presented pre-gestational diabetes mellitus and plasma fructosamine level were registered in the medical records prior to the ultrasound exam. The first measurement recorded was compared with the result of routine fetal echocardiography, carried out by a specialist physician of the service. The presence or absence of echocardiographic findings of congenital cardiopathies (EFCC) was related to plasma levels of fructosamine by the mean t-test and its accuracy for EFCC was verified by the ROC curve. Plsama fructosamine concentrations of 2.68, 2.9 and 2.23 mmol/L, which are, respectively, the local reference laboratory values, the value of the kit employed for measurement and the one of highest overall accuracy, were discussed as the cut-off values. RESULTS: EFCC was found in 52.3% of the fetuses. The first measurement of fructosamine, during the prenatal care period, was performed, on average, at 20.4±8.0 weeks of pregnancy. The maternal concentration ability of the fructosamine to identify fetuses with EFCC was significant (p<0.0001) and had an area under the ROC curve of 0.78 (95%CI=0.66-0.89). The 2.9 mmol/L plasma concentration of fructosamine revealed EFCC with better specificity, but with a higher percentage of false-negative results (96.8 and 55.9%). Values above 2.68 mmol/L were associated with a probability of 4.6 to identify fetuses with EFCC compared with lower values, with 58.8% of sensitivity and 87.1%, specificity. The value of 2.23 mmol/L proved to be the most overall accurate of the three values suggested, with a sensitivity of 88.2% in the identification of fetuses with echocardiographic abnormalities. CONCLUSIONS: it is possible to use a second trimester plasma fructosamine level to refer high risk pregnant women to a reference center of fetal echocardiography. These findings are important for the management of women with diabetes mellitus who initiate late prenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):66-66
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):66-66
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):66-71
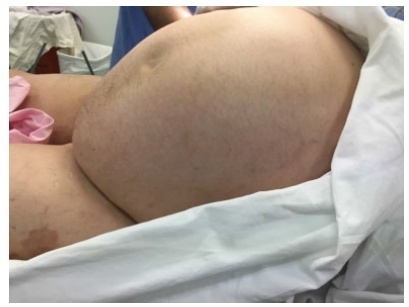
Uterine leiomyoma is themost prevalent benign type of gynecological tumor. It affects more than 80% of women worldwide and, within this group, more than 50% may be asymptomatic. However, large fibroid volumes may be associated with symptoms of extrinsic compression, and most of the cases do not present atypical cells. We present the case of a 49-year-old woman who underwent a total abdominal hysterectomy of a 13.5-kg uterine leiomyoma with no malignancies at histopathology and review the literature about giant uterine leiomyomas and their clinical repercussion. We concluded that large volumes do not always pose a threat regarding malignancy; however, future molecular studies are needed to investigate giant uterine fibroids.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):66-70
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200005
PURPOSE: To ascertain the seroprevalence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B (HBV), toxoplasmosis and rubella infections in pregnant women in northwestern Paraná. METHODS: We conducted a retrospective study based on the results of serological screening during prenatal care of 1,534 patients during the first half of 2010. We included only results from the first prenatal exam and with a simultaneous search for IgG and IgM antibodies to rubella and toxoplasmosis. Serology was performed by microparticle enzyme immunoassay (MEIA). Data were analyzed statistically by the χ² test, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: HIV positivity was 0.3%, positivity of HBV serology (HbsAg) was 0.5%, reactivity to IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii was 1.1%, and reactivity to IgG antibodies was 59.0%. For rubella, no patient was positive for IgM, and IgG reactivity was 99.6%. Data analysis showed no statistical association between seroprevalence and patient age, except for the frequency of anti-T. gondii IgG, which was higher in the 30 to 44 year age group. CONCLUSION: The prevalence of these infectious diseases in pregnant women from northwestern Paraná is comparable to that observed in other regions of Brazil.