Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(10):658-658
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):658-663
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100005
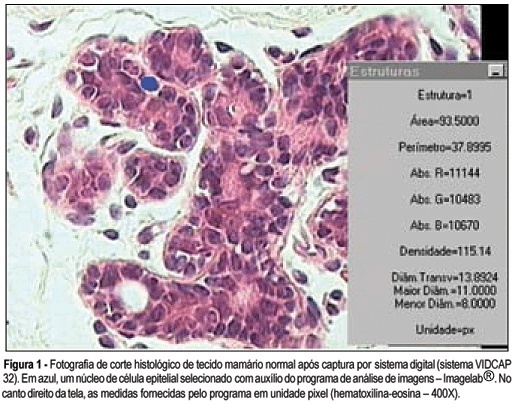
PURPOSE: to analyze breast tissue of postmenopausal women before and after six months of continuous combined estrogen-progestin replacement therapy (0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogens associated with 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate). METHODS: all patients were evaluated before treatment and considered eligible to receive the drug. The material was obtained from the upper outer left quadrant, through a percutaneous large-core breast biopsy. Epithelial density and nuclear volume on hematoxylin-eosin-stained plates were evaluated for the morphological study. Morphometry was graphically analyzed by optical microscopy (400X) after acquisition of image by a digital image-capturing system (Vidcap 32) and image analysis system (Imagelab 2000 Software®). RESULTS: after six months of estrogen-progestin replacement therapy, there was a significant increase in nuclear volume in late postmenopausal women (103.6 to 138.1 µm³). There was no difference in epithelial density with the treatment (before 0.08 and later 0.10). CONCLUSIONS: estrogen-progestin combined replacement therapy for six months induced an enhacement in nuclear volume of breast epithelial cells, suggesting an increase in their metabolic activity. However, it is important to emphasize that this finding was observed only in late postmenopausal women. The increased nuclear volume could precede other events that confirm the stimulation of cellular proliferation by these hormones.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):658-659
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):658-659
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
To identify the most effective procedures recommended for the prevention of preeclampsia.
A systematic review was performed in the following databases: Pubmed/MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane and LILACS via the Virtual Health Library (VHL). A manual search was also performed to find additional references. The risk of bias, the quality of the evidence, and the classification of the strength of the recommendations were evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
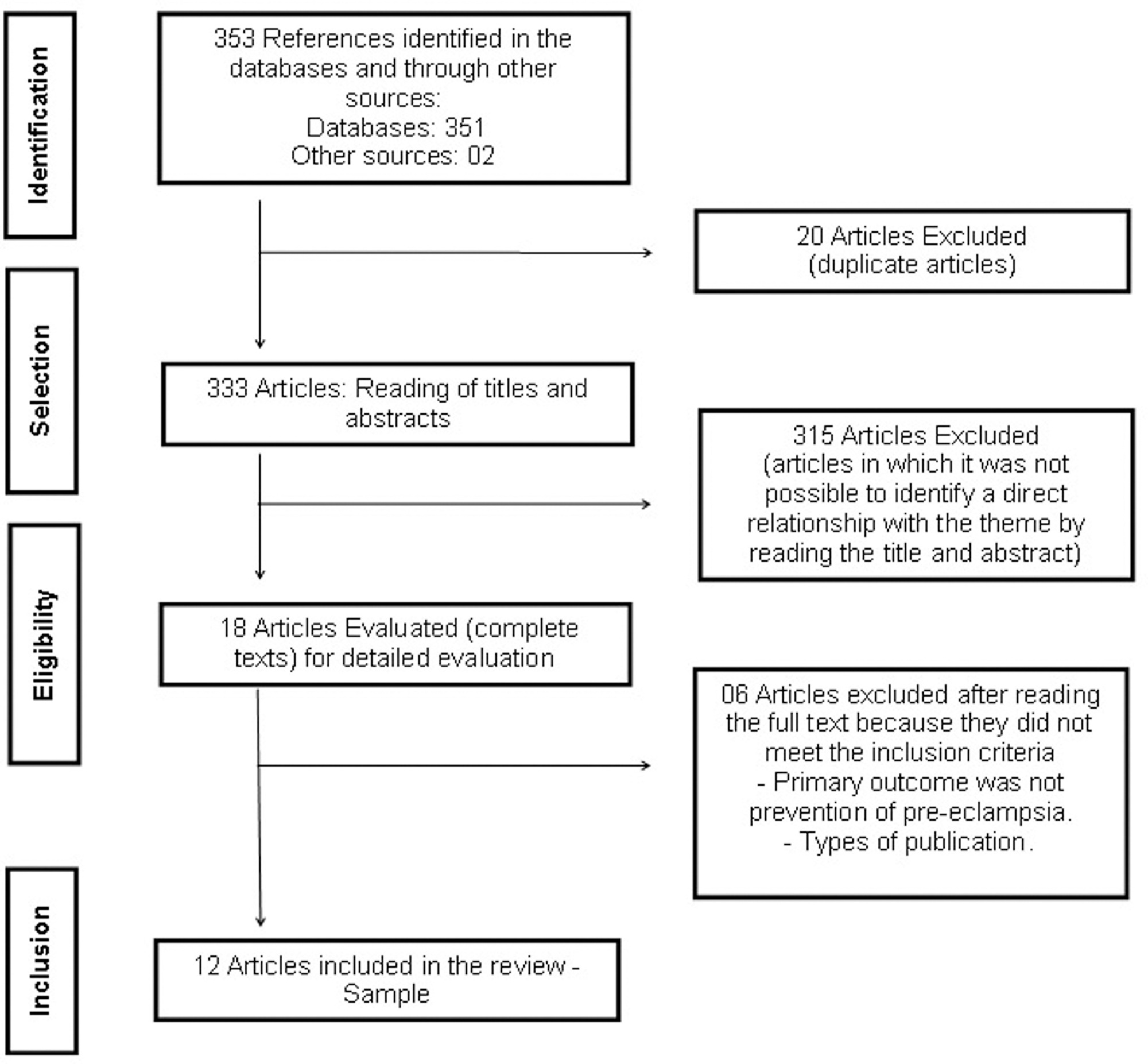
In the initial search in the databases, the total number of articles retrieved was 351, and 2 were retrieved through the manual search; after duplicate articles were removed, 333 citations remained. After a thorough review of the titles and abstracts, 315 references were excluded. Accordingly, 18 articles were maintained for selection of the complete text (phase 2). This process led to the exclusion of 6 studies. In total, 12 articles were selected for data extraction and qualitative synthesis.
The articles selected for the study were analyzed, and we inserted the synthesis of the evidence in the online software GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) (McMaster University and Evidence Prime Inc. All right reserved. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontário, Canada); thus, it was possible to develop a table of evidence, with the quality of the evidence and the classification of the strength of the recommendations.
In total, seven studies recommended the individual use of aspirin, or aspirin combined with calcium, heparin or dipyridamole. The use of calcium alone or in combination with phytonutrients was also highlighted. All of the studies were with women at a high risk of developing preeclampsia.
According to the studies evaluated, the administration of aspirin is still the best procedure to be used in the clinical practice to prevent preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(10):659-665
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000008
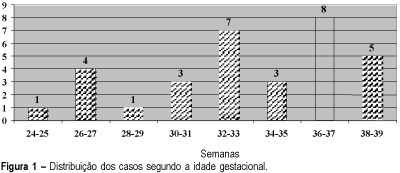
Purpose: evaluation of perinatal outcome of brain-sparing effect detected by color Doppler. Methods: brain-sparing effect was detected in 32 fetuses at the Ultrasound Service of the Center for Integral Attention to Women's Health at Campinas State University (UNICAMP). The diagnosis of brain-sparing effect was made when the ratio between middle cerebral artery and umbilical artery pulsatility indexes was below one (IPACM/IPAU <1). The measurement was obtained with color Doppler equipment Toshiba SSH-140A. Results: admission to neonatal intensive care unit (ICU) was necessary in 26 fetuses (89.6%). The number of days in ICU varied from 1 to 83 days, with a mean of 22 days. Fetal mortality rate was 3 in 32 (9.4%) and perinatal mortality was 9 in 29 (31%). Considering the gestational age by the Capurro method, the incidence of birth below 36 weeks was 21 in 32 (65.6%). Intrauterine growth restriction occurred in 71.8% of the cases and hypoglycemia in 44.8%. Conclusions: brain-sparing effect is a condition in which the fetus is at serious risk of adverse perinatal outcome and Doppler studies might be helpful in the obstetric management.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):659-662
The importance of the C677T mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene in infertile women remains controversial.
To evaluate if the MTHFR C677T mutations are more frequent in infertile women, and if they can be associated with the occurrence of infertility in the Brazilian population.
This case-control study included 130 infertile women consulting at a private clinic betweenMarch 2003 andMarch 2005 (data previously published), and 260 fertile women attending the family planning outpatient clinic of our institution between April 2012 and March 2013.
The Chi-squared and Fisher Exact tests were used to evaluate the association between the presence of the MTHFR C677T mutation and a history of infertility.
The frequency of the mutation was of 58.5% for the case group (n = 76) and of 49.2% for the fertile controls (n = 128). The mutation was homozygous in 13 women in the case group (10%) and in 23 of the fertile women in the control group (8.8%). These differences were not statistically significant.
These results suggest that the presence of the MTHFR C677T mutation does not constitute a risk factor for infertility, even when themutation is homozygous. Further studies are needed to confirm whether research on this mutation should be considered unnecessary in women with infertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):66-71
To evaluate the impact of sexual function (SF) in the quality of life (QoL) of women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI).
Case-control study in which 80women with POIwere evaluated using estrogen plus progestogen therapy, compared with 80 women matched by age (2 years) and presenting preserved gonadal function. Sexual function was evaluated using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and the QoL was evaluated using theWorld Health Organization's (WHO) QoL assessment instrument (WHOQoL-BREF).
The mean age of the women with POI and of the control group was 38.4 ± 7.3 years and 38.1 ± 7.3 years respectively. The QoL, was worse among the POI group, and there were significant differences in the physical (63.4 ± 17.4 and 72.7 ± 15.2 respectively, p = 0.0004) and psychological (63.2 ± 14.6 and 69.3 ± 13.9 respectively, p = 0.0075) domains among this group when compared with the control group. Women with POI presented significantly lower arousal, lubrication, orgasm and satisfaction, more dyspareunia and a worse FSFI scores when compared with the control group. All aspects of SF correlate directly with the worsening of the QoL regarding social relationships.
Women with POI showed worse QoL and SF than the control group. The psychological aspects (desire, excitement, orgasm and sexual satisfaction) of SF had greater influence on the parameters of the QoL, while the physical aspects (pain and lubrication) had a low impact on the QoL. The poor SF in women with POI is directly correlated with a worsening acrossmultiple domains of the QoL; however, the negative impact is particularly important in the social domain. These results suggest that the improvement in sexuality can improve the social interactions of women with POI.