Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
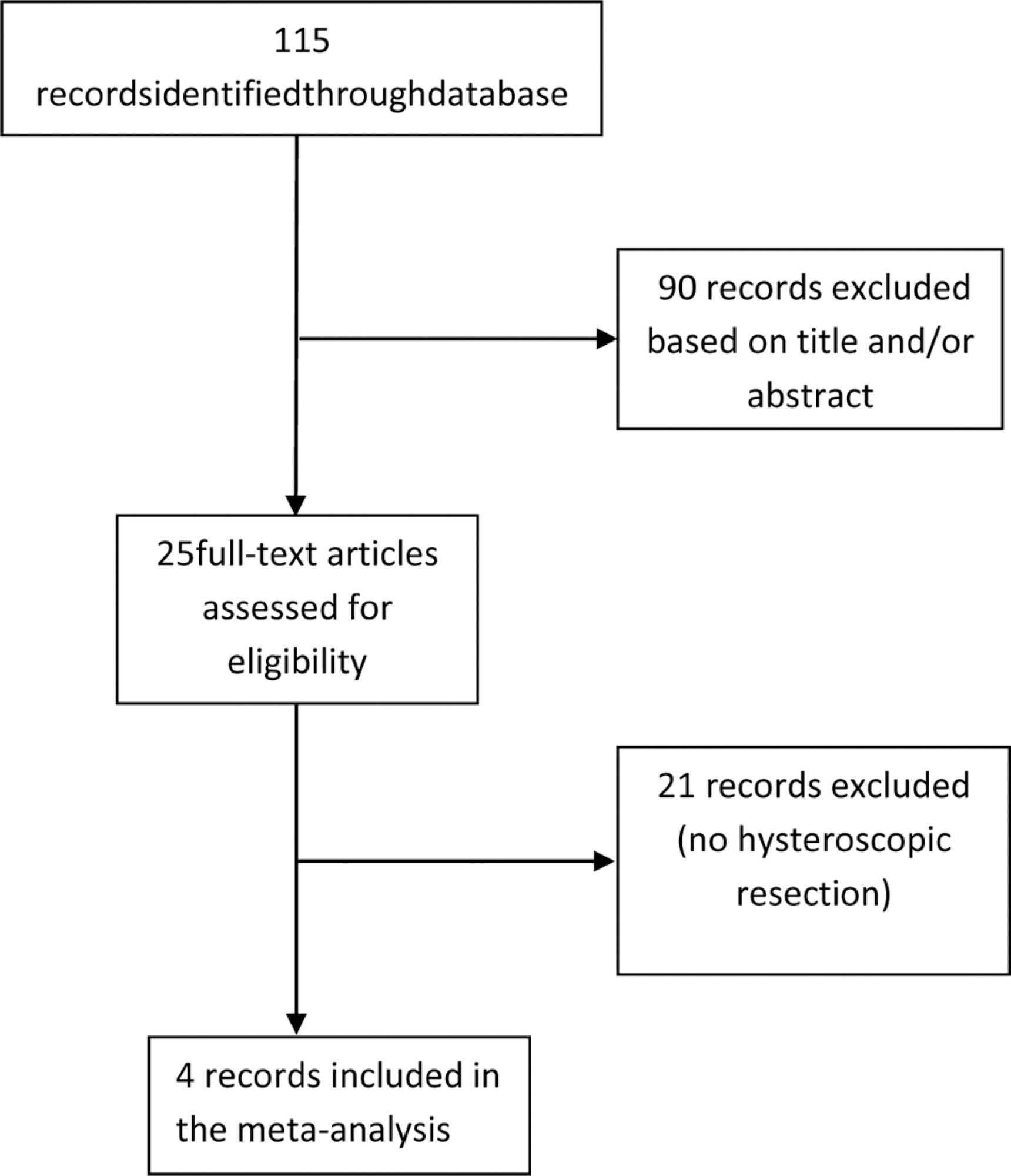
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: - 3.81; 95%;CI : - 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: - 65.90; 95%;CI: - 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):65-65
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):65-69
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200002
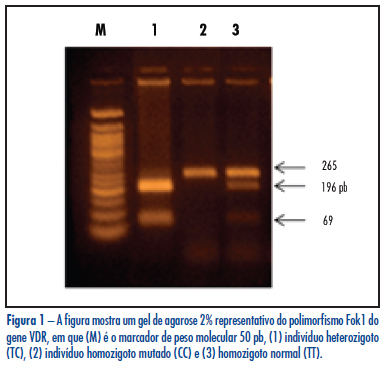
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 in infertile women with endometriosis and Control and its relation to the disease. METHODS: a case-control study that included 147 infertile women with endometriosis and 154 fertile women without endometriosis as Control. Fok1 polymorphism (rs10735810, T2C), which promotes a T/C exchange in exon 2 of the VDR gene, was identified by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), that involves the combination of amplification by PCR and digestion with restriction endonuclease. The χ2 test was used to compare allele and genotype frequencies between groups. All p-values were two-tailed and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: the TT, TC and CC genotype frequencies of VDR Fok1 polymorphism were 44.2%, 46.9% and 8.9% in infertile women with endometriosis and 41.6%, 50% and 8.4% in the Control Group. No significant difference was found (p=0.8), even when the patients were subdivided according to the stage of endometriosis (p=0.3 for minimal and mild endometriosis and p=0.2 for moderate and severe endometriosis). Alleles T and C were present, respectively, in 67.6% and 32.3% of infertile women with endometriosis (p=0.8), in 63.5% and 36.5% of women with minimal/mild endometriosis (p=0.5), in 72.5% and 27.5% of women with moderate/severe endometriosis (p=0.2), and in 66.6% and 33.4% of the Control Group. No statistically significant difference was found among any groups and the Control. CONCLUSION: the results suggest that VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 does not confer genetic susceptibility to endometriosis-associated infertility in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):65-70
The objective of this study is to assess the performance of cytopathology laboratories providing services to the Brazilian Unified Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde - SUS) in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil.
This descriptive study uses data obtained from the Cervical Cancer Information System from January to December 2012. Three quality indicators were analyzed to assess the quality of cervical cytopathology tests: positivity index, percentage of atypical squamous cells (ASCs) in abnormal tests, and percentage of tests compatiblewith high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs). Laboratories were classified according to their production scale in tests per year≤5,000; from 5,001 to 10,000; from 10,001 to 15,000; and 15,001. Based on the collection of variables and the classification of laboratories according to production scale, we created and analyzed a database using Microsoft Office Excel 97-2003.
In the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais, 146 laboratories provided services to the SUS in 2012 by performing a total of 1,277,018 cervical cytopathology tests. Half of these laboratories had production scales≤5,000 tests/year and accounted for 13.1% of all tests performed in the entire state; in turn, 13.7% of these laboratories presented production scales of > 15,001 tests/year and accounted for 49.2% of the total of tests performed in the entire state. The positivity indexes of most laboratories providing services to the SUS in 2012, regardless of production scale, were below or well below recommended limits. Of the 20 laboratories that performed more than 15,001 tests per year, only three presented percentages of tests compatible with HSILs above the lower limit recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health.
The majority of laboratories providing services to the SUS in Minas Gerais presented quality indicators outside the range recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):65-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200004
To analyze the relationships among gestational risk, type of delivery and
immediate maternal and neonatal repercussions.
A retrospective cohort study based on secondary data was conducted in a
university maternity hospital. A total of 1606 births were analyzed over a 9-month
period. Epidemiological, clinical, obstetric and neonatal characteristics were
compared according to the route of delivery and the gestational risk characterized
on the basis of the eligibility criteria for high clinical risk. The occurrence of
maternal and neonatal complications during hospitalization was analyzed according
to gestational risk and cesarean section delivery using univariate and
multivariate logistic analysis.
The overall rate of cesarean sections was 38.3%. High gestational risk was
present in 50.2% of births, mainly represented by hypertensive disorders and fetal
malformations. The total incidence of cesarean section, planned cesarean section
or emergency cesarean section was more frequent in pregnant women at gestational
high risk (p<0.001). Cesarean section alone did not influence maternal outcome,
but was associated with poor neonatal outcome (OR 3.4; 95%CI 2.7-4.4). Gestational
high risk was associated with poor maternal and neonatal outcome (OR 3.8; 95%CI
1.3-8.7 and OR 17.5; 95%CI 11.6-26.3, respectively). In multivariate analysis, the
ratios were maintained, although the effect of gestational risk has determined a
reduction in the OR of the type of delivery alone from 3.4 (95%CI 2.7-4.4) to 1.99
(95%CI 1.5-2.6) for adverse neonatal outcome.
Gestational risk was the main factor associated with poor maternal and neonatal
outcome. Cesarean delivery was not directly associated with poor maternal outcome
but increased the chances of unfavorable neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):65-66
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):65-65
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):65-70
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100010
PURPOSE: to identify risk factors involved in Candida sp vulvovaginitis in an exploratory study using an intentional sample. METHODS: a cross-sectional study with a sample of 135 textile female workers living in Criciúma, South Brazil, between July and September 2002. Oral interview and physical examination were performed by a single gynecologist and vaginal swabs were collected for culture and plated on Sabouraud agar. Epi-Info, version 6.0 was used to analyze the collected data. Prevalence ratios were calculated with a 95% confidence interval. A multivariable analysis of the data by logistic regression and data entry using the SPSS, version 10.0 computer program, was performed. RESULTS: the prevalence of Candida sp vulvovaginitis confirmed by culture in this sample was 19.3%. The prevalence of clinical vulvovaginitis was 17.0% (sensitivity of 38% and specificity of 88%). Significant risk factors for clinically manifest vulvaginitis were the use of hormones and age between 25-34 years and for culture-proven Candida sp vulvovaginitis, regular menstrual cycle. CONCLUSIONS: the overall prevalence of Candida sp vulvovaginitis was 19.3%. A regular menstrual cycle was the main risk factor for Candida sp vulvovaginitis showing the existence of a relationship between menstrual cycle and Candida sp vulvovaginitis. This finding should be better investigated by a cohort study with a larger sample and correlated with blood hormone levels throughout the menstrual cycle.