Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):633-638
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200006
PURPOSE: to compare macro and microscopically, surgical uterine sutures in female rabbits, after caesarean section utilizing separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture stitches. METHODS: three New Zealand female rabbits in their first pregnancy were used. The caesarean section was carried out at the 26th day of gestation and three incisions were performed in each uterus. The hysterorrhaphy was performed with a 00 Vicryl® thread, and a different suture technique was employed for each incision. Total hysterectomy and adnexectomy were done at the 60th day post-delivery with the preservation of eventual adhesions for the evaluation of the surgical scars. The extent of scar retraction, amount of fibrin deposit and the suture integrity were evaluated through macroscopy. For the evaluation through microscopy, hematoxylin eosin technique was used for cellular colorimetry, and Masson's trichrom to evidence collagen. The statistical non-parametric Friedman's test was employed for the matching hypothesis, and Fisher's exact test to verify the homogeneity of the techniques (level of significance: 5%). RESULTS: a total of 18 scars were obtained (six scars per suture). The following mean values were obtained for the longitudinal (0.5/0.4/0.5, p=0.069) and transversal retraction degrees (0.3/0.4/0.3, p=0.143) respectively for separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture techniques. All sutures presented regular fibrin deposit, no adhesions and integral absorption of the stitches. The mean value of the blood vessels (158.5/139.3/172.1; p=0.293), fibroblasts (351.6/345.8/354.3; p=0.311) and of collagen percentage (44.0/45.5/48.5; p=0.422) were calculated through microscopy, respectively for separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture techniques. CONCLUSIONS: the type of hysterorrhaphy technique of caesarean section in female rabbits did not generate any significant statistical difference in the macroscopic and microscopic parameters evaluated.
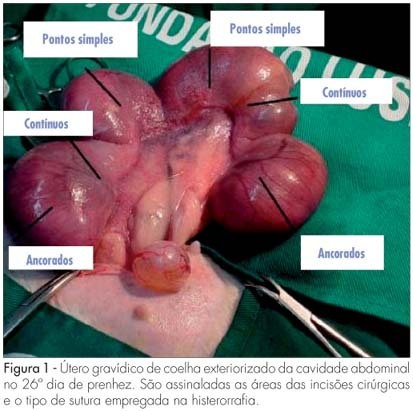
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):633-642
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100002
PURPOSE: to verify the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of some ultrasonographic measurements in the diagnosis of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). METHODS: transvaginal ultrasound measurements of the bladder neck descent, urethral mobility and urethrovesical funneling caused by urination effort were performed in 40 women with SUI and in 40 women from a control group. Age, parity and the number of pregnancies were different in both groups. Several cut points were performed to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of these measurements as a diagnostic tool for SUI. The urodynamic results were used as gold standard. Univariated analysis was done using Yates chi2 Test and Pearson chi2 Test. RESULTS: in the best cut point for bladder neck descent measurements, sensitivity was 40%, specificity was 72% and accuracy was 57%; in the best cut point for urethral mobility measurements, sensitivity was 40%, specificity was 70% and accuracy was 55%; in the best cut point for urethrovesical funneling measurements, sensitivity was 58%, specificity was 48% and accuracy was 52%; in the best cut point for the addition of the differences of these three measurements, sensitivity was 32%, specificity was 62% and accuracy was 48%. CONCLUSION: vaginal ultrasonography was not a valid diagnostic method for stress urinary incontinence in the present study.
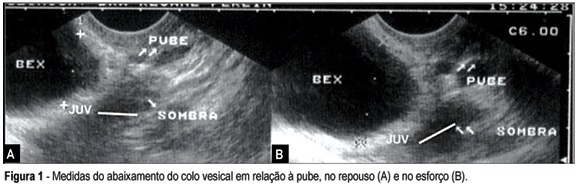
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):633-639
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800007
PURPOSE: to check whether there were differences in some social indicators between adolescent and adult pregnant women in the city of Ribeirão Preto, from January 1992 to December 1996. METHODS: the information was obtained from hospital discharge forms and was analyzed at the Hospital Data Processing Center of the FMRP-USP. The analyzed parameters were: number and types of deliveries, category of hospital admission, occupation, and obstetric diagnosis. The 6.04a text processor Epi-Info System, a data bank and statistics of epidemiology produced by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (Atlanta, GA, USA), and Dbase IV were used to process the information. The association between variables was tested by the chi² test, with level of significance set at 5%, using the GraphPad Prism version 2.0, 1995 software. RESULTS: a total of 43,253 deliveries occurred during this period, among which 7,134 (16.5%) corresponded to adolescent deliveries, while 36,119 (83.5%) to adult deliveries. The number of deliveries by adolescent girls increased 25.5% along this period. The proportion of adolescent deliveries in the unified health system category of admission increased, and it was higher than that of the adults'. Only 14.1% of the adolescents belonged to the economically active population, comparing with 34.8% of the adults. Only 6.8% of the adolescents were students, while 79.0% were house-workers or had a nonpaid occupation. In the analyzed period, the ratio of vaginal delivery increased among the adolescents, as compared to that of the adults. The ratio of cesarean delivery persisted stable and higher among the adults. Premature delivery and false labor were significantly more frequent among the adolescents. CONCLUSION: the number of deliveries increased among the adolescents, and most of them were normal. The ratio of admission by the unified health system category and that of vaginal delivery were higher among the adolescents. There were more adolescents without an economically active work. Thus, we recommend strategies to prevent adolescent pregnancy, mainly among the poor population.
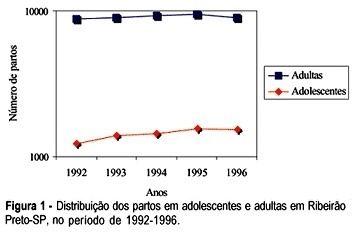
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):634-641
To identify clinical, microscopic, and biochemical characteristics that differentiate cytolytic vaginosis (CV) from vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).
The present cross-sectional study analyzed the vaginal contents of 24 non-pregnant women aged 18 to 42 years who were attended at the Genital Infections Clinic at Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher da Universidade Estadual de Campinas (CAISM-UNICAMP). They were diagnosed either with (CV = 8, VVC = 8) or without vulvovaginitis or vaginal dysbiosis (controls). The socio-demographic, clinical, and gynecological data were obtained from a detailed patient interview. Samples of the vaginal contents were collected for analysis of vaginal pH, gram stain, and specific fungal culture. The Kruskal-Wallis and Fisher exact tests were used to compare the differences between the groups. Odds ratios were used to compare the categorical variables. The significance level was considered at p < 0.05.
Both women with CV and VVC had a lumpy vaginal discharge (p = 0,002) and vaginal hyperemia (p = 0.001), compared with controls. The inflammatory process was more intense in the VVC group (p = 0.001). In the CV group, there was statistical significance for the lactobacillus amount (p = 0.006), vaginal epithelium lysis (p = 0.001), and vaginal pH (p = 0.0002).
Cytolytic vaginosis and VVC diagnoses rarely differ on clinical characteristics but have different laboratorial findings. The present study highlights the importance of conducting an accurate investigation through laboratory tests rather than clinical criteria to avoid misdiagnosis.
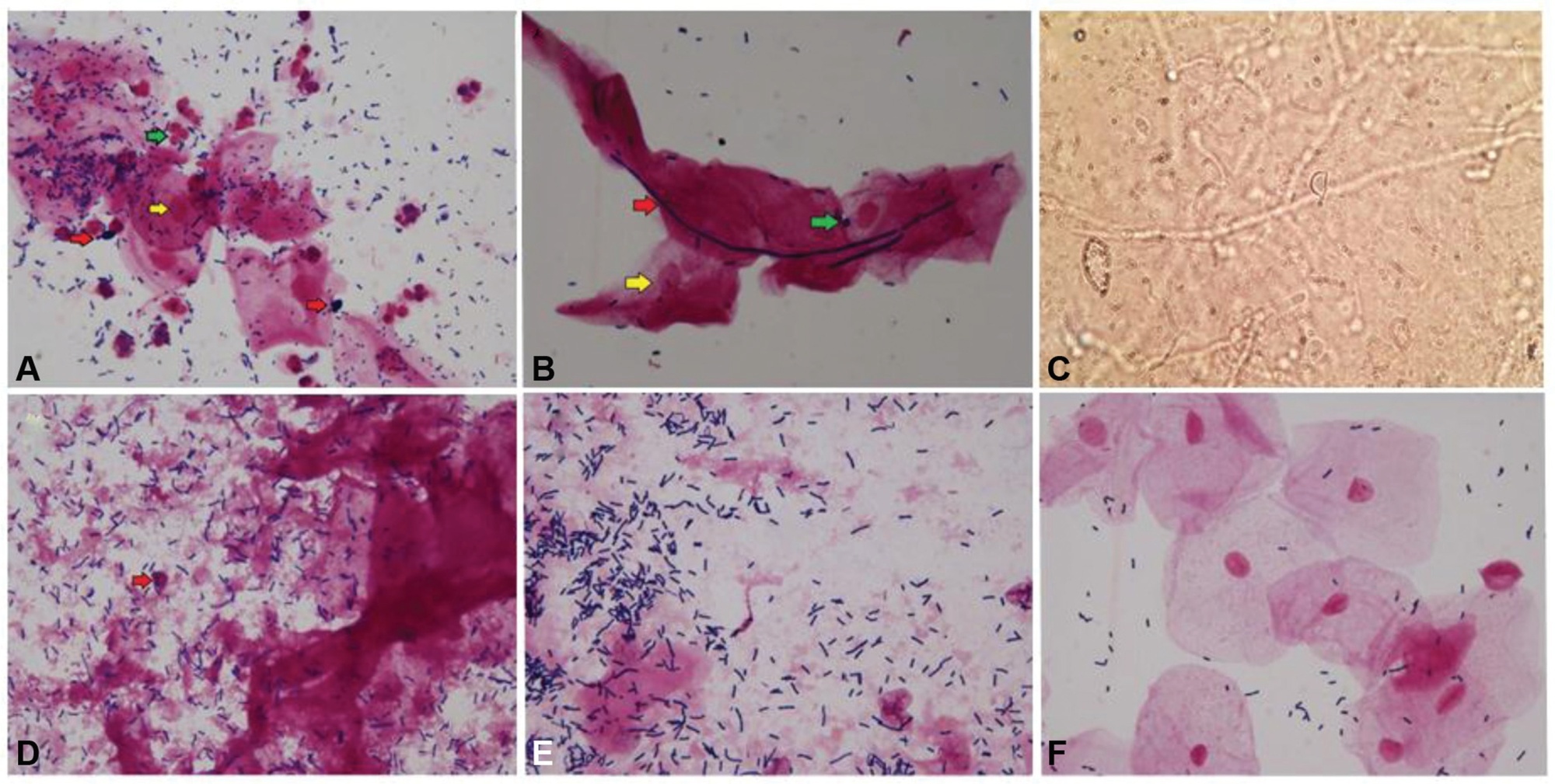
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):635-637
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):635-635
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):635-635
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):636-636