Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(2):109-114
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000200006
PURPOSE: to evaluate maternal and perinatal outcomes of premature rupture of membranes up to the 26th week of gestation. METHODS: retrospective analysis of the cases of premature rupture of membranes up to the 26th week of gestation, without signs of labor or treatment for this condition before admission, followed up at the Obstetric Pathology Infirmary of the "Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand", Federal University of Ceará, from January 1994 to December 1999. The cases with gestational age less than 22 weeks and birth weight lower than 500 g were excluded. Premature rupture of membranes was confirmed by sterile speculum examination. In doubt, amniotic fluid crystallization test and pH determination were performed. All pregnant women underwent ultrasound examination to determine gestational age and amniotic fluid volume. Data concerning the result of gestation and consequences for the mother, fetus and neonate were analyzed. RESULTS: a total of 29 cases of premature rupture of membranes fulfilled inclusion criteria. The mean gestational age at rupture of membranes was 22 weeks. The mean duration of the latency period was 21.7 days. There Were 22 spontaneous vaginal and 3 induced deliveries, besides 4 cesarean sections. In six pregnant women there were signs of infection before labor. Antibiotics were administered in 37.9% of the cases and corticosteroids in 6.9%. No patient underwent tocolysis. There were 3 fetal and 25 neonatal deaths. Only one infant survived. This child remained at the neonatal care unit for 19 days due to infection and respiratory distress syndrome. There was no maternal death. CONCLUSION: the premature rupture of membranes up to the 26th week of gestation has been a fatal discase for fetuses and newborns in our institution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):109-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200009
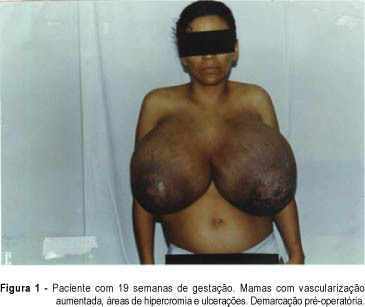
A rare case of bilateral benign phyllode tumor of the breast with fast growth during pregnancy and reaching great dimensions is presented. The patient was submitted to bilateral mastectomy on the 20th week of pregnancy. She had a good postoperative evolution and vaginal delivery occurred on the 40th week, when a healthy boy was born. The clinical and surgical features, the pathologic findings and the evolution of pregnancy are discussed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1090-1093
To describe the clinical results of patients admitted and managed as cases of placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) at a Central American public hospital and the influence of the prenatal diagnosis on the condition.
A retrospective analysis of PAS patients treated at Hospital Bertha Calderón Roque, in Managua, Nicaragua, between June 2017 and September 2021. The diagnostic criteria used were those of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique, FIGO, in French). The population was divided into patients with a prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of PAS (group 1) and those whose the diagnosis of PAS was established at the time of the caesarean section (group 2).
During the search, we found 103 cases with a histological and/or clinical diagnosis of PAS; groups 1 and 2 were composed of 51 and 52 patients respectively. Regarding the clinical results of both groups, the patients in group 1 presented a lower frequency of transfusions (56.9% versus 96.1% in group 2), use of a lower number of red blood cell units (RBCUs) among those undergoing transfusions (median: 1; interquartile range: [IQR]: 0–4 versus median: 3; [IQR]: 2–4] in group 2), and lower frequency of 4 or more RBCU transfusions (29.4% versus 46.1% in group 2). Group 1 also exhibited a non-significant trend toward a lower volume of blood loss (1,000 mL [IQR]: 750–2,000 mL versus 1,500 mL [IQR]: 1,200–1,800 mL in group 2), and lower requirement of pelvic packing (1.9% versus 7.7% in group 2).
Establishing a prenatal diagnosis of PAS is related to a lower frequency of transfusions. We observed a high frequency of prenatal diagnostic failures of PAS. It is a priority to improve prenatal detection of this disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1094-1101
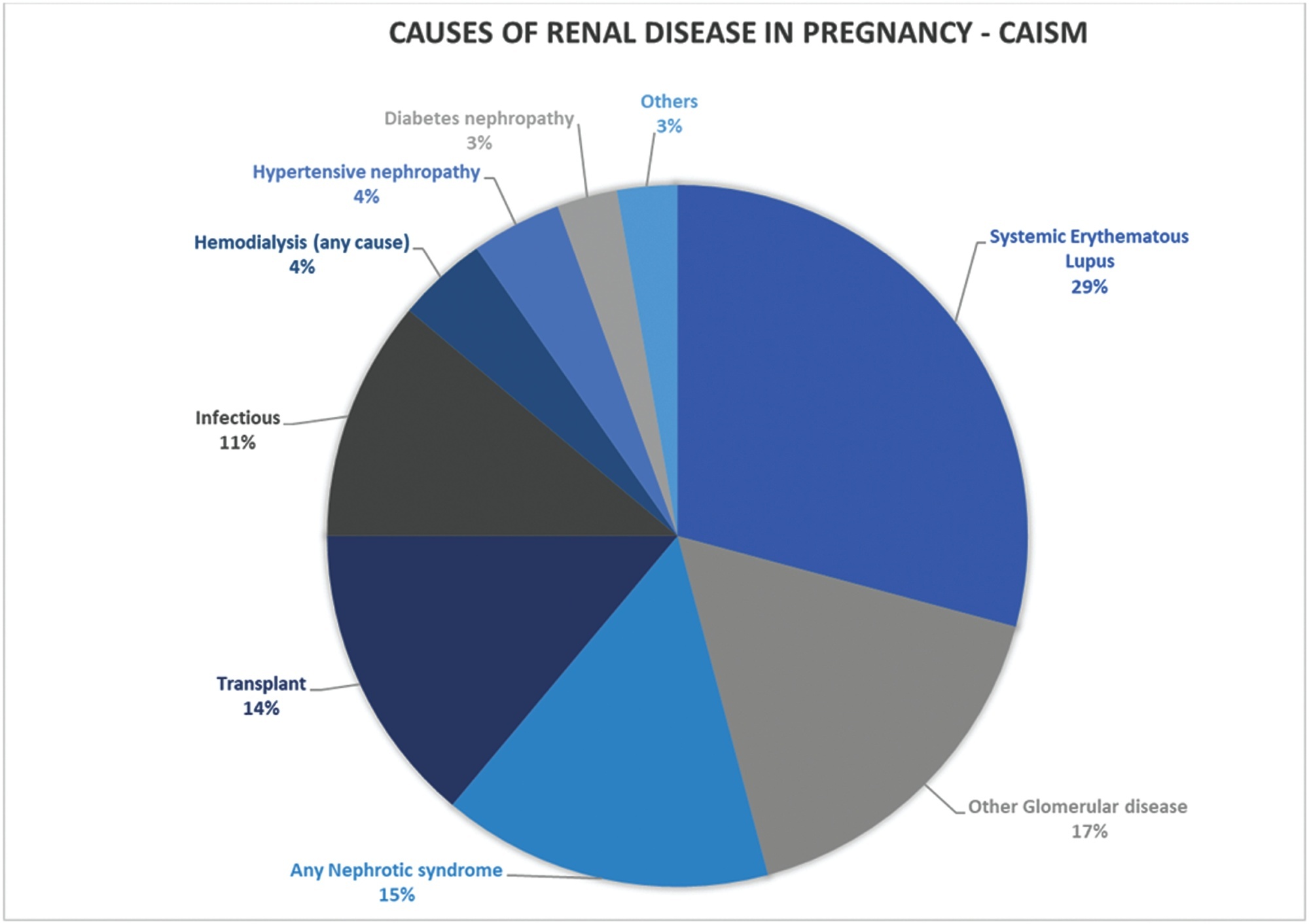
To assess maternal and neonatal outcomes in women with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy.
A retrospective cohort of pregnant women with CKD was followed at the Women's Hospital of Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Brazil, between 2012 and 2020. Variables related to disease etiology, treatment duration, sociodemographic variables, lifestyle, other associated diseases, obstetric history, and perinatal outcomes were assessed. The causes of CKD were grouped into 10 subgroups. Subsequently, we divided the sample according to gestational age at childbirth, as preterm and term births, comparing maternal and neonatal outcomes, and baseline characteristics as well as outcomes among such groups.
A total of 84 pregnancies were included, in 67 women with CKD. Among them, six pregnancies evolved to fetal death, five to miscarriage, and one was a twin pregnancy. We further analyzed 72 single pregnancies with live births; the mean gestational age at birth was 35 weeks and 3 days, with a mean birth weight of 2,444 g. Around half of the sample (51.39%) presented previous hypertension, and 27.7% developed preeclampsia. Among the preterm births, we observed a higher frequency of hypertensive syndromes, longer maternal intensive care unit (ICU) stay in the postpartum period, higher incidence of admission to the neonatal ICU, higher neonatal death, lower 5-minute Apgar score, and lower birth weight.
This study demonstrates increased adverse outcomes among pregnancies complicated by CKD and expands the knowledge on obstetric care among such women in an attempt to reduce maternal risks and identify factors related to prematurity in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(1):11-20
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may cause irreversible organ damage. Pregnancy with SLE may have severe life-threatening risks. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of severe maternal morbidity (SMM) in patients with SLE and analyze the parameters that contributed to cases of greater severity.
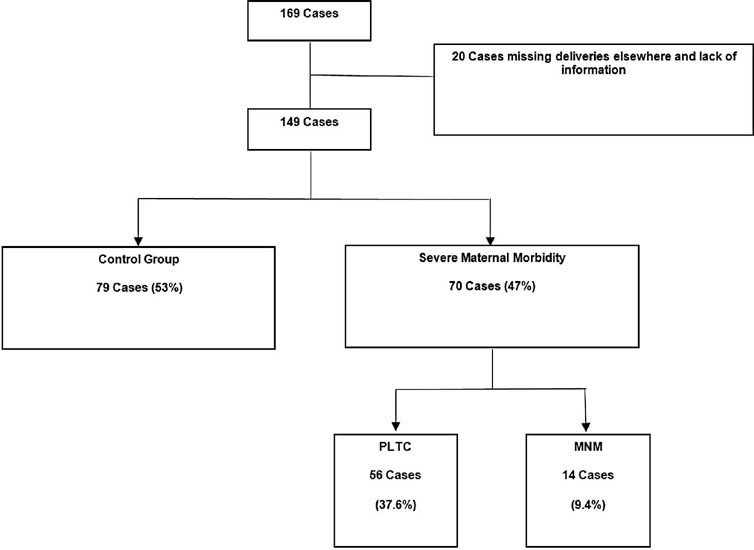
This is a cross-sectional retrospective study from analysis of data retrieved from medical records of pregnant women with SLE treated at a University Hospital in Brazil. The pregnant women were divided in a control group without complications, a group with potentially life-threatening conditions (PLTC), and a group with maternal near miss (MNM).
The maternal near miss rate was 112.9 per 1,000 live births. The majority of PLTC (83.9%) and MNM (92.9%) cases had preterm deliveries with statistically significant increased risk compared with the control group (p = 0.0042; odds ratio [OR]: 12.05; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.5–96.6 for the MNM group and p = 0.0001; OR: 4.84; 95%CI: 2.2–10.8 for the PLTC group). Severe maternal morbidity increases the risk of longer hospitalization (p < 0.0001; OR: 18.8; 95%CI: 7.0–50.6 and p < 0.0001; OR: 158.17; 95%CI: 17.6–1424,2 for the PLTC and MNM groups, respectively), newborns with low birthweight (p = 0.0006; OR: 3.67; 95%CI: 1.7–7.9 and p = 0.0009; OR: 17.68; 95%CI: 2–153.6) for the PLTC and MNM groups, respectively] as well as renal diseases (PLTC [8.9%; 33/56; p = 0.0069] and MNM [78.6%; 11/14; p = 0.0026]). Maternal near miss cases presented increased risk for neonatal death (p = 0.0128; OR: 38.4; 95%CI: 3.3–440.3]), and stillbirth and miscarriage (p = 0.0011; OR: 7.68; 95%CI: 2.2–26.3]).
Systemic lupus erythematosus was significantly associated with severe maternal morbidity, longer hospitalizations, and increased risk of poor obstetric and neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(1):11-18
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000100003
PURPOSE: to describe adverse perinatal outcomes in patients with fetal blood flow centralization, using the relationship between the pulsatility indexes of the middle cerebral and umbilical arteries (MCAPI/UAPI), and between the resistance indexes of the middle cerebral and umbilical arteries (MCARI/UARI), as well as to compare both diagnostic indexes. METHODS: 151 pregnant women with diagnosis of blood flow centralization, attended to at the maternity hospital of Universidade Estadual de Campinas, whose delivery occurred up to 15 days after the ultrasonographic diagnosis, were included. It was considered as adverse perinatal outcomes: Apgar index lower than 7 at the fifth minute, permanence in neonatal ICU, small fetus for the gestational age, severe fetal suffering, perinatal death, hypoglycemia, polycythemia, necrotizing enterocolitis, brain hemorrhage, lung hemorrhage, anemia, septicemia, hyaline membrane disease, convulsive syndromes, hyperreflexia syndrome and kidney insufficiency. Rates of the perinatal adverse outcomes (PAO) for the brain-placentary ratios have been compared, using Fisher's exact or Pearson's χ2 tests, at 5% significance level. Adverse perinatal outcomes according to the gestational age have been evaluated using the Cochrane-Armitage test for trend. RESULTS: the adverse perinatal outcomes for the group with the two indexes altered were: 62.5% of the newborns needed to be placed in an ICU, 75.2% were small for the gestational age (SGA), 35.3% were under severe fetal suffering, 84.4% had hypoglycemia, 8.3% polycythemia, 4.2% necrotizing enterocolitis, and 2.1% brain hemorrhage. There has been significant association between the MCAPI/UAPI and MCARI/UARI ratios along the gestational age, and the need for neonatal intensive care, small fetuses for the gestational age, septicemia, necrotizing enterocolitis, kidney insufficiency, hyaline membrane disease, and anemia. There has been no significant difference between the two indexes of adverse perinatal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):11-16
To evaluate the accuracy of the diagnosis of fetal heart diseases obtained through ultrasound examinations performed during the prenatal period compared with the postnatal evaluation.
A retrospective cohort study with 96 pregnant women who were attended at the Echocardiography Service and whose deliveries occurred at the Complexo Hospitalar Santa Casa de Porto Alegre, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Risk factor assessment plus sensitivity and specificity analysis were used, comparing the accuracy of the screening for congenital heart disease by means of obstetrical ultrasound and morphological evaluation and fetal echocardiography, considering p < 0.05 as significant. The present study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Institution.
The analysis of risk factors shows that 31.3% of the fetuses with congenital heart disease could be identified by anamnesis. The antepartum echocardiography demonstrated a sensitivity of 97.7%, a specificity of 88.9%, and accuracy of 93% in the diagnosis of congenital heart disease. A sensitivity of 29.3% was found for the obstetric ultrasound, of 54.3% for themorphological ultrasound, and of 97.7% for the fetal echocardiography. The fetal echocardiography detected fetal heart disease in 67.7% of the cases, the morphological ultrasound in 16.7%, and the obstetric ultrasound in 11.5% of the cases.
There is a high proportion of congenital heart disease in pregnancies with no risk factors for this outcome. Faced with the disappointing results of obstetric ultrasound for the detection of congenital heart diseases and the current unfeasibility of universal screening of congenital heart diseases through fetal echocardiography, the importance of the fetal morphological ultrasound and its performance by qualified professionals is reinforced for a more appropriate management of these pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(1):11-15
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000100003
PURPOSE: The present study examined the relationship between some clinical variables and quality of life in a group of patients with endometriosis. METHODS: A total of 130 women seen at a multidisciplinary center specializing in gynecology endometriosis in 2008 participated in the study. This was a cross-sectional study conducted with a convenience sample. The diagnosis of endometriosis was performed by biopsy according to the criteria of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. The clinical and demographic data were collected from the patients' records. Pain intensity was assessed by a visual numerical scale (0-10), and data on the quality of life were collected using the SF-36. Data analysis consisted of descriptive and inferential statistical tests, Spearman correlation coefficient and Kruskal-Wallis test to compare scores between groups. Nonparametric tests were used for analysis because data were not normally distributed. RESULTS: The patients were 21 to 54 years of age [ or = 34, standard diversion (SD)=6.56], 87% had a university degree, and 75% were married. Seventeen percent reported cases of endometriosis in the family. The average time of onset of symptoms was 4.5 years (SD=6.6), 63% of patients were in stage 3 or 4 of endometriosis 36% of patients had severe or disabling dysmenorrhea and the average intensity of pain according to a visual numerical scale was of 5.6 (SD=3.5). Results suggest that the staging of the disease did not determine the intensity of pain. The time of onset of symptoms also showed no relationship to pain intensity and SF-36 scores. On the other hand, the intensity of pain was associated with lower scores on some scales of the SF-36. CONCLUSION: Patients with endometriosis had lower scores of quality of life than the general population and lower than those of some other diseases.
or = 34, standard diversion (SD)=6.56], 87% had a university degree, and 75% were married. Seventeen percent reported cases of endometriosis in the family. The average time of onset of symptoms was 4.5 years (SD=6.6), 63% of patients were in stage 3 or 4 of endometriosis 36% of patients had severe or disabling dysmenorrhea and the average intensity of pain according to a visual numerical scale was of 5.6 (SD=3.5). Results suggest that the staging of the disease did not determine the intensity of pain. The time of onset of symptoms also showed no relationship to pain intensity and SF-36 scores. On the other hand, the intensity of pain was associated with lower scores on some scales of the SF-36. CONCLUSION: Patients with endometriosis had lower scores of quality of life than the general population and lower than those of some other diseases.