Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):107-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200006
PURPOSE: we report a small series of pregnant women who underwent gastric bypass surgery for severe obesity, with a review of the literature on this topic. METHODS: five consecutive cases of pregnancy after gastroplasty between 2001 and 2004 were evaluated, and clinical, laboratory and therapeutic features were considered. Patients were 30 to 34 years old and all had been submitted to gastroplasty by the Capella technique. The outcomes for both the pregnant woman and the fetus were evaluated. A search of the English language literature was done through MEDLINE and Web of Science databases with the following terms: gastroplasty, gastric bypass surgery, bariatric surgery, and pregnancy. RESULTS: all 5 pregnancies were singleton. No major obstetric complications were observed and there were no premature or lowbirth weight infants. CONCLUSION: our data suggest that pregnancy following gastroplasty is safe for mother and fetus. However, since information about this topic is limited, further investigations are required to establish appropriate recommendations concerning the follow-up of these pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300003
To evaluate the impact of sexual and reproductive health theme insertion in the undergraduate medical curriculum at a Brazilian public university.
We developed an instrument for cognitive assessment in sexual and reproductive health based on the subjects addressed in the optional curriculum component Reproductive Health, resulting in an objective multiple choice test containing 27 items. The selected topics were: human, sexual and reproductive rights (HSRR), sexuality, institutional violence, gender, sexual violence, conception, contraception, abortion/legal interruption of pregnancy, maternal mortality and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - HIV/AIDS. The subjects were grouped into three dimensions of knowledge: HSRR, legal/institutional and biomedical. Two multivariate models were adjusted in the analysis of covariance.
The study included 183 students, 127 of the group who took the elective curriculum course reproductive health (RH Group) and 56 who did not (Non-RH Group). Ninety-six students (52.5%) were males and 87 (47.5%) were females. Mean age was 24.7±1.9 years for the RH Group and 24.4±2.6 for the Non-RH Group. The average performance of the SR Group was higher than that of Non-RH subjects regarding the following subjects: HSRR, sexuality, institutional violence, sexual violence, abortion/legal interruption, and STDs - HIV/AIDS. There was no gender difference in performance, except for the theme maternal mortality, in which males scored worse than females (6.9±0.2 and 7.8±0.2, respectively; p<0.05).
The participation of students in the elective curriculum component Reproductive Health was associated with better performance in some dimensions of cognitive assessment, suggesting a positive impact of this initiative on general medical education.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(3):107-110
Summary
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000005
PURPOSE: to evaluate which method is the best to determine pre-surgically the size of breast cancer: clinical examination, mammography or ultrasonography, using as a reference the anatomopathological exam. METHODS: this study has included 184 patients with palpable-or-not breast lesions, detected by mammography and ultrasonography, that were submitted to surgical resection of the tumor, with histopathological diagnosis of breast cancer. The same examiner evaluated clinically the largest tumoral diameter, through clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography, and the measurements obtained by each method were correlated with the maximum diameter obtained by the anatomopathological exam. The comparative analysis has been done by Pearson's correlation coefficient (r). RESULTS: Pearson's correlation coefficient between the anatomopathological and the clinical exams was 0.8; between the anatomopathological exam and the mammography, 0.7; and between anatomopathological exam and ultrasonography 0.7 (p<0.05). Pearson's correlation coefficients among the methods evaluated were also calculated and r=0.7 was obtained between clinical exam and mammography, r=0.8 between clinical examination and utrasonograhy, and r=0.8 between mammography and ultrasonography (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography have presented high correlation with the anatomopathological measures, besides high correlations among themselves, what seems to show that they may be used as equivalent methods in the pre-surgical evaluation of the breast tumoral size. Nevertheless, due to specific limitations of each method, clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography should be seen as complementary to each other, in order to obtain a more accurate measurement of the breast cancer tumor.
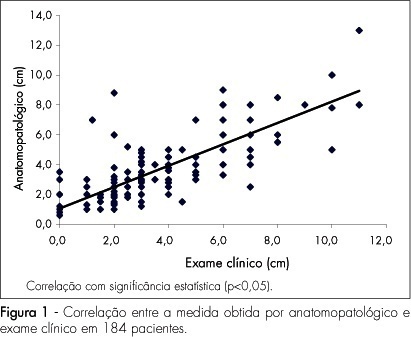
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000300003
PURPOSE: To analyze the influence of maternal nutritional status, weight gain and energy consumption on fetal growth in high-risk pregnancies. METHODS: A prospective study from August 2009 to August 2010 with the following inclusion criteria: puerperae up to the 5th postpartum day; high-risk singleton pregnancies (characterized by medical or obstetrical complications during pregnancy); live fetus at labor onset; delivery at the institution; maternal weight measured on the day of delivery, and presence of medical and/or obstetrical complications characterizing pregnancy as high-risk. Nutritional status was assessed by pregestational body mass index and body mass index in late pregnancy, and the patients were classified as: underweight, adequate, overweight and obese. A food frequency questionnaire was applied to evaluate energy consumption. We investigated maternal weight gain, delivery data and perinatal outcomes, as well as fetal growth based on the occurrence of small for gestational age and large for gestational age neonates. RESULTS: We included 374 women who were divided into three study groups according to newborn birth weight: adequate for gestational age (270 cases, 72.2%), small for gestational age (91 cases, 24.3%), and large for gestational age (13 cases, 3.5%). Univaried analysis showed that women with small for gestational age neonates had a significantly lower mean pregestational body mass index (23.5 kg/m², p<0.001), mean index during late pregnancy (27.7 kg/m², p<0.001), and a higher proportion of maternal underweight at the end of pregnancy (25.3%, p<0.001). Women with large for gestational age neonates had a significantly higher mean pregestational body mass index (29.1 kg/m², p<0.001), mean index during late pregnancy (34.3 kg/m², p<0.001), and a higher proportion of overweight (30.8%, p=0.02) and obesity (38.5%, p=0.02) according to pregestational body mass index, and obesity at the end of pregnancy (53.8%, p<0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed the index value during late pregnancy (OR=0.9; CI95% 0.8-0.9, p<0.001) and the presence of hypertension (OR=2.6; 95%CI 1.5-4.5, p<0.001) as independent factors for small for gestational age. Independent predictors of large for gestational age infant were the presence of diabetes mellitus (OR=20.2; 95%CI 5.3-76.8, p<0.001) and obesity according to body mass index during late pregnancy (OR=3.6; 95%CI 1.1-11.7, p=0.04). CONCLUSION: The maternal nutritional status at the end of pregnancy in high-risk pregnancies is independently associated with fetal growth, the body mass index during late pregnancy is a protective factor against small for gestational age neonates, and maternal obesity is a risk factor for large for gestational age neonates.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):107-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200008
Purpose: the aim of the present work was to study the chronic action of the antiemetic domperidone on the pregnancy of albino rats. Methods: fifty albino, pregnant Wistar rats were randomly allocated to five groups: GI (control I) = intact rats; GII (control II) = rats receiving the drug vehicle (distilled water) by gavage at the same schedule of the experimental groups; rats in groups GIII, GIV and GV were treated with domperidone by gavage, 2, 6 and 12 mg/kg per day, respectively, divided into 4 daily doses, always in 1 ml of distilled water, from time zero up to the 20th day of pregnancy. The evolution of body weight gain was followed throughout and the animals were sacrificed at term (20th day) by deep ether anesthesia. Number of fetuses, placenta and implantation sites, placenta and fetus weight, fetal malformations and maternal and fetal mortality were evaluated. Results: we observed only intrauterine fetal mortality with 14, 26 and 32 in 74, 60 and 57 newborns of the groups III, IV and V, respectively. Conclusion: though the results of animal experimentation cannot directly be transposed to human conditions, this paper calls attention to the need for a safe judgement when prescribing domperidone to a first-trimester pregnant patient in order to reduce her emetic crises.
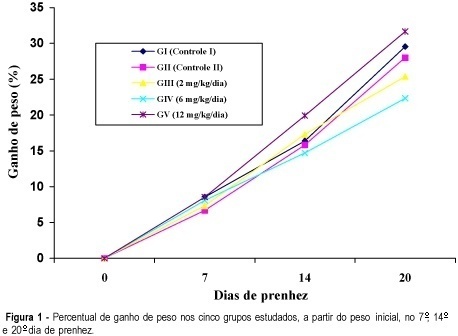
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(2):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000200006
Purpose: to analyze the effects of prenatal and perinatal complications and the neurological development of surviving twins when the other had died in utero. Methods: fourteen cases of twin pregnancies where one of the twins had died during the pregnancy were analyzed. These patients gave birth between 1988 and 1994 and were subsequently followed-up by the Department of Obstetrics, Pathology Division, at the Hospital das Clínicas, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. Data from prenatal and perinatal records as well as findings from the deceased twins' autopsies were analyzed. In 1996, requests were made for the children to have a neurological examination as part of the study. The examination included developmental assessment and pathological signs in the motor, sensory and sensitivy areas and superior cortical functions such as praxis and agnosia. Results: ten of the fourteen contacted subjects complied with the request for neurological examination. Of the ten examined children only one had abnormal neurological findings, presenting a light degree of spastic paresis of the left leg. The pregnancy evaluation showed five cases of monochorionic placenta and one case of monoamnionic pregnancy; six of the fourteen cases reached full-term. In six cases (42.8%) one of the fetus died during the second trimester and in the other they died during the third trimester. Only one newborn, who had Apgar 0 at the first minute, developed neurological sequelae. Conclusion: the neurological problem of one fetus may be a consequence of the perinatal complications that this fetus developed. The other newborns did not develop sequelae, possibly because of the conservatory management, trying to make the pregnancy reach 32 weeks or more, thus decreasing the complications of preterm delivery.