Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1032-1039
To determine how many patients underwent screening for diabetes mellitus (DM) in the puerperium after a diagnosis of gestational DM (GDM) and which factors were related to its performance.
The present is a prospective cohort study with 175 women with a diagnosis of GDM. Sociodemographic and clinico-obstetric data were collected through a questionnaire and a screening test for DM was requested six weeks postpartum. After ten weeks, the researchers contacted the patients by telephone with questions about the performance of the screening. The categorical variables were expressed as absolute and relative frequencies. The measure of association was the relative risk with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), and values of p ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant and tested through logistic regression.
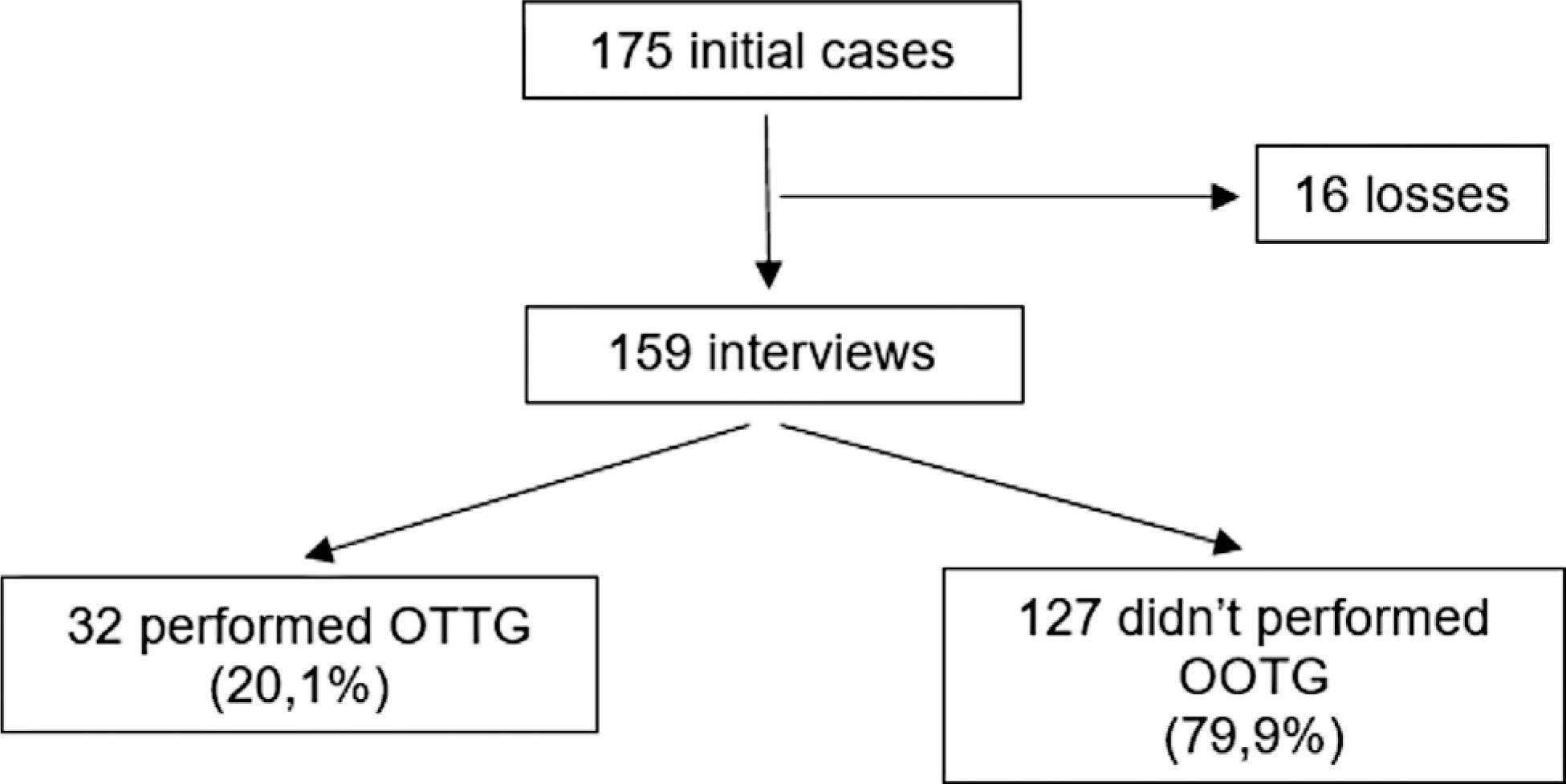
The survey was completed by 159 patients, 32 (20.1%) of whom underwent puerperal screening. The mean age of the sample was of 30.7 years, and most patients were white (57.9%), married (56.6%), and had had 8 or more years of schooling (72.3%). About 22.6% of the patients used medications to treat GDM, 30.8% had other comorbidities, and 76.7% attended the postnatal appointment. Attendance at the postpartum appointment, the use of medication, and the presence of comorbidities showed an association with the performance of the oral glucose tolerance test in the puerperium.
The prevalence of screening for DM six weeks postpartum is low in women previously diagnosed with GDM. Patients who attended the postpartum consultation, used medications to treat GDM, and had comorbidities were the most adherent to the puerperal screening. We need strategies to increase the rate of performance of this exam.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):104-108
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):104-115
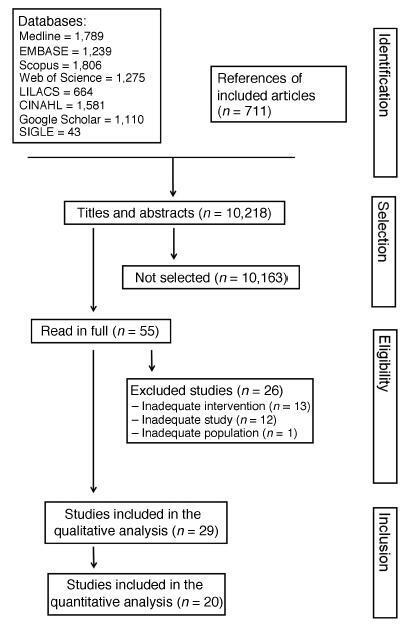
Diabetes during pregnancy has been linked to unfavorable maternal-fetal outcomes. Human insulins are the first drug of choice because of the proven safety in their use. However, there are still questions about the use of insulin analogs during pregnancy. The objective of the present study was to determine the effectiveness of insulin analogs compared withhuman insulin in the treatment of pregnant women with diabetes througha systematic review withmeta-analysis. The search comprised the period since the inception of each database until July 2017, and the following databases were used:MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE, ISIWeb of Science, LILACS, Scopus, SIGLE andGoogle Scholar.We have selected 29 original articles: 11 were randomized clinical trials and 18 were observational studies.We have explored data from 6,382 participants. All of the articles were classified as having an intermediate to high risk of bias. The variable that showed favorable results for the use of insulin analogs was gestational age, with a mean difference of - 0.26 (95 % confidence interval [CI]: 0.03-0.49; p = 0.02), but with significant heterogeneity (Higgins test [I2] = 38%; chi-squared test [χ2] = 16.24; degree of freedom [DF] = 10; p = 0.09). This result, in the clinical practice, does not compromise the fetal well-being, since all babies were born at term. There was publication bias in the gestational age and neonatal weight variables. To date, the evidence analyzed has a moderate-to-high risk of bias and does not allow the conclusion that insulin analogs are more effective when compared with human insulin to treat diabetic pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1040-1046
The purpose was to assess the rates of postoperative complications and the need of temporary stoma of laparoscopic surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis in a referral center.
The surgical indication, type of operation, operative time, length of hospital stay, need for a temporary stoma, rate of conversion to open surgery, postoperative complications were evaluated.
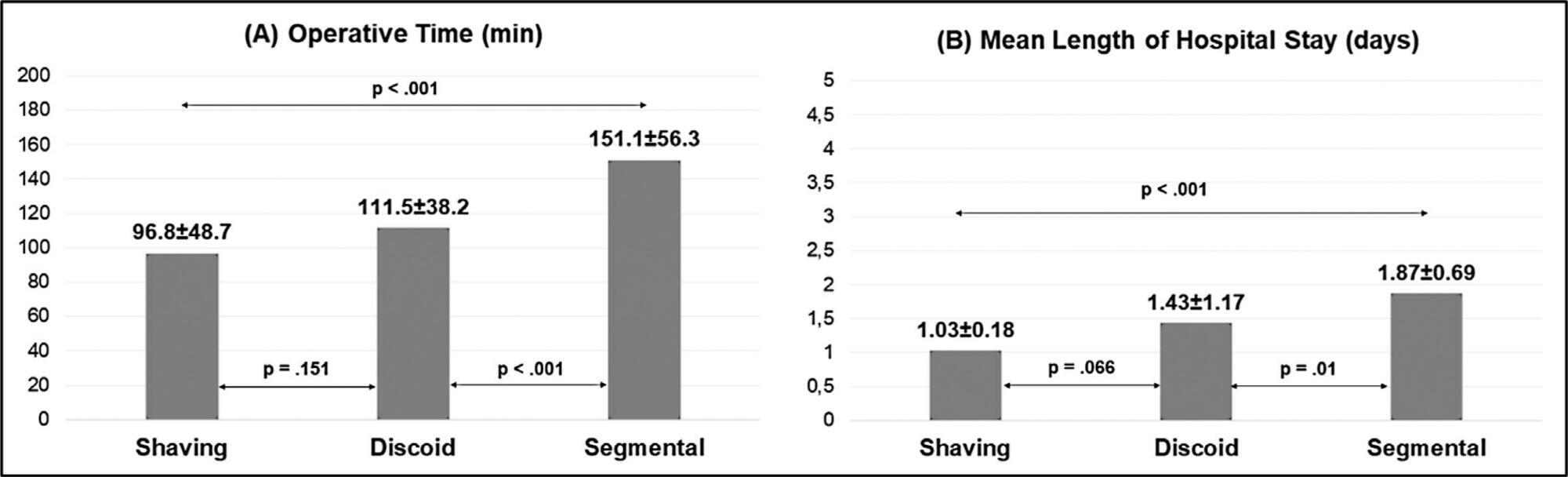
One-hundred and fifty patients were included. The average duration of surgery was significantly longer for segmental resection (151 minutes) than for disc excision (111.5 minutes, p < 0.001) and shaving (96.8 minutes, p < 0.001). Patients with segmental resection had longer postoperative lengths of hospital stay (1.87 days) compared with patients with disc excision (1.43 days, p < 0.001) and shaving (1.03 days, p < 0.001). A temporary stoma was performed in 2.7% of patients. Grade II and III postoperative complications occurred in 6.7% and 4.7% patients, respectively.
Laparoscopic intestinal resection has an acceptable postoperative complication rate and a low need for a temporary stoma.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1047-1051
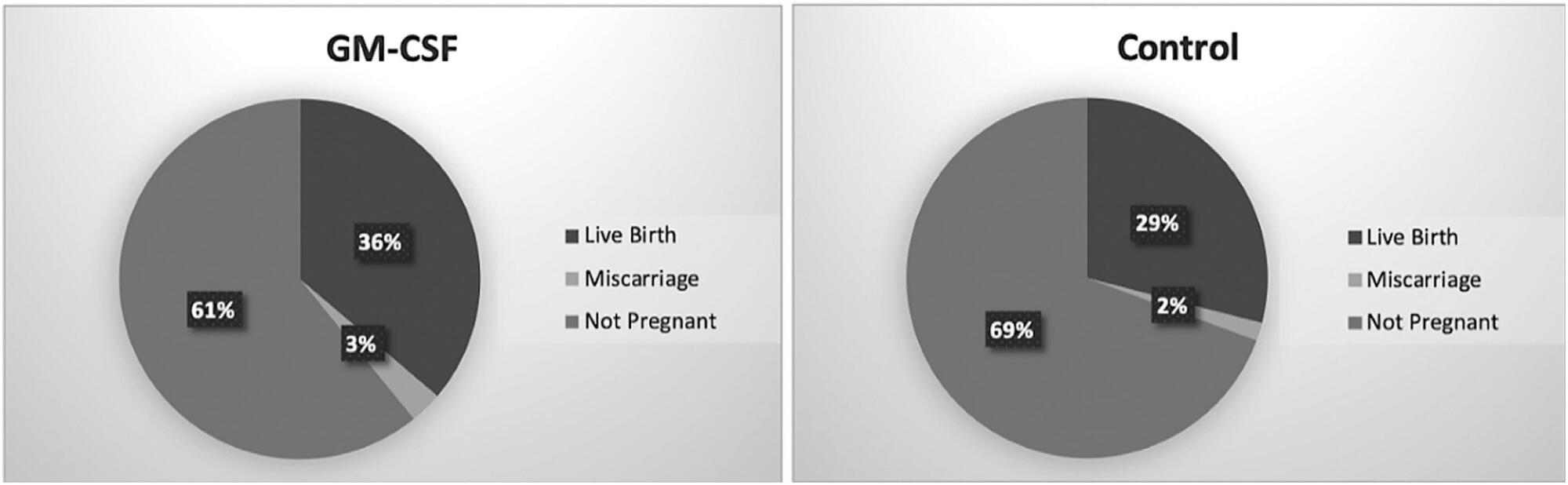
The use of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-containing medium, which is a commercial medium that is used for cultivation of embryos in in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments, has been suggested to increase the efficiency of this procedure in patients with previous multiple unsuccessful attempts. In this retrospective study, we analyzed GM-CSF-containing embryo culture media compared with traditional culture media in terms of development of embryos, pregnancy, and ongoing pregnancy success and live birth rates.
This is a prospective case control study conducted in a single center. A total of 131 unexplained infertility patients were included in the study. A cohort of 69 patients whose embryos were cultured in GM-CSF-containing medium and a control group of 62 age-matched patients whose embryos were cultured in conventional Sage One Step medium were included in the study. The major study outcomes were achievement of pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy rate at 12 weeks of gestation.
The pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy rates of the patients whose embryos were cultured in GM-CSF-containing medium were 39.13% and 36.23%, respectively. These were higher than the rates of the control group, which were 30.65% and 29.03%, respectively, although this difference was not statistically significant. In addition, the 5th-day embryo transfer percentage in the GM-CSF group was higher than in the control group (34.78% versus 27.4%).
The main findings of our study were that there was no difference between the GM-CSF-enhanced medium and the control group in terms of our major study outcomes. However, blastomere inequality rate and embryo fragmentation rates were lower in the GM-CSF group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(2):105-109
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000200008
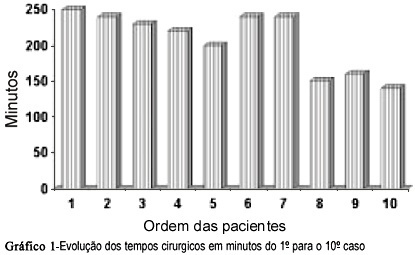
The authors describe their experience with videolaparoscopic tubal anastomosis in 10 selected patients operated from June 1994 to February 1996. The time of the first surgery was 4 hours and 30 minutes and the last , 2 hours and 30 minutes. The time was different according to the change of auxiliary team. Half of the reanastomoses were isthmic- isthmic. The minimum size of the remaining tubes was 5cm on each side. We used 7-0 and 6-0 polyglycolic acid monofilament for suture. The tube patency was tested by hysterosalpingogram 3 months after surgery, and it was shown that 88.8% of the operated tubes were free. The patients considered able to become pregnant were followed up for a short period of time and 4 of them became pregnant. The hospitalization lasted 24 hours and there were no surgical or anesthetic complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):105-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion reported by a sample of Brazilian women interviewed in the National Demographic Health Survey of 1996. METHODS: this was a secondary analysis of the Brazilian DHS-96 database, with information from interviews with a representative sample of 12,612 women about their reproductive life, focusing on the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion in the last five years and the associated factors for the various regions of the country and for Brazil as a whole. The sampling method was implemented with a strategy selection in two stages, one for the households and the other for women. The prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion was estimated for Brazil and regions, and the socio-demographic characteristics of the women were analyzed as a function of the abortion's experience. A multinomial regression model analysis was used for the identification of factors independently associated with both types of abortion; their OR and respective 95% CI are reported. RESULTS: the prevalence of reported spontaneous abortion was 14% and the prevalence of induced abortion was 2.4% for the country as a whole. The state with the highest prevalence of induced abortion was Rio de Janeiro with 6.5%, followed by the Northeast region with 3.1%. The places with the lowest prevalence were the state of São Paulo and the South region. Both spontaneous and induced abortion showed higher prevalences with increasing age of the women studied. Being from the urban area (OR=1.5; 95%CI=1.0-2.3), having had more than one live child (OR=2.2; 95%CI=1.5-3.2) and being non-white (OR=1.4; 95%CI=1.0-1.8) were the main risk factors for induced abortion. CONCLUSIONS: the non-modifiable risk factors for induced abortion identified in this study indicate the need for improvement of educational and contraceptive actions, with priority for these specific demographic groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):105-109
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005201
To determine whether paraspinal block reduces pain scores compared to placebo in women with chronic pelvic pain refractory to drug therapy.
Subjects with chronic pelvic pain due to benign conditions and refractory to drug therapy were invited to participate in a randomized, double blind, superiority trial at a tertiary reference center. Subjects were randomly allocated to receive paraspinal anesthetic block with 1% lidocaine without epinephrine or placebo (control). Lidocaine was injected along the spinal process of the painful segment in the supra- and interspinal ligaments using a 25G X 2" needle. Placebo consisted of introduction of the needle in the same segment without injecting any substance. The main outcome measured was the pain score based on a visual analog scale at T0 (baseline), T1 (within 15 min after the procedure) and T2 (one week after the procedure). Data were statistically analyzed by ANOVA and the 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
Mean age was similar for both groups, i.e., 51.2 (paraspinal anesthetic block) and 51.8 years (control). A blind examiner measured the degree of pain according to the visual analog scale from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain imaginable). Based on the visual analog scale, the mean pain scores of the paraspinal anesthetic block group at T0, T1 and T2 were 5.50 (SD=2.92; 95%CI 3.84-7.15), 2.72 (SD=2.10; 95%CI 1.53-3.90), and 4.36 (SD=2.37; 95%CI 1.89-6.82), respectively. The difference between T0 and T1 was statistically significant, with p=0.03.
Paraspinal anesthetic block had a small effect on visual analog scale pain score immediately after the injections, but no sustained benefit after one week. Further studies are needed to determine the efficacy of paraspinal anesthetic block with different lidocaine doses for the treatment of visceral pain of other causes.