Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):10-17
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000100003
PURPOSE: to describe to emotional process experienced with termination of pregnancy after the diagnosis of lethal fetal malformation. METHODS: thirty-five pregnant women who underwent termination of pregnancy for lethal fetal anomaly after judicial permission were interviewed. The most frequent fetal malformation was anencephaly (71.5%). The patients were submitted to an open interview as soon as the diagnosis of fetal malformation was confirmed, allowing them to express their feelings and stimulating them to think about asking for termination of pregnancy. The mean time spent until the judicial agreement was 16.6 days. The women who requested and were submitted to the procedure of abortion were invited to return for psychological evaluation after 30-60 days. At this moment, a semi-structured interview was performed to find the emotional aspects and feelings that existed. RESULTS: thirty-five patients were interviewed. The decision-making feelings about termination of pregnancy were negative for 60%, 51.4% declared that they had no doubts about the assumed decision and 65.7% declared that their own opinion was more important for decision than anyone else's. Most of the women (89%) affirmed to remember the facts about the procedure that they experienced, 91% affirmed that they would have the same attitude in the case of another similar situation in the future and 60% declared that they would advise someone to opt for termination of pregnancy if asked about the same situation. CONCLUSIONS: the anguish experienced showed that the process of thinking is very important for the decision-making process and posterior satisfaction with the assumed posture. The psychological follow-up allows to review the moral and cultural values in order to help the decision-making process with the aim of minimizing the suffering.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):10-15
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100003
PURPOSES: To investigate the effect of an individualized and supervised exercise program for the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) in the postpartum period of multiparous women, and to verify the correlation between two methods used to assess PFM strength. METHODS: An open clinical trial was performed with puerperal, multiparous women aged 18 to 35 years. The sample consisted of 23 puerperal women divided into two groups: Intervention Group (IG, n=11) and Control Group (CG, n=12). The puerperal women in IG participated in an eight-week PFM exercise program, twice a week. The puerperal women in CG did not receive any recommendations regarding exercise. PFM strength was assessed using digital vaginal palpation and a perineometer. The statistical analysis was performed using the following tests: Fisher's exact, c², Student's t, Kolmogorov-Smirnov for two samples, and Pearson's correlation coefficient. Significance was defined as p<0.05. RESULTS: The participants' mean age was 24±4.5 years in IG and 25.3±4 years in CG (p=0.4). After the exercise program, a significant difference was found between the groups in both modalities of muscle strength assessment (p<0.001). The two muscle strength assessment methods showed a significant correlation in both assessments (1st assessment: r=0.889, p<0.001; 2nd assessment: r=0.925, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: The exercise program promoted a significant improvement in PFM strength. Good correlation was observed between digital vaginal palpation and a perineometer, which indicates that vaginal palpation can be used in clinical practice, since it is an inexpensive method that demonstrated significant correlation with an objective method, i.e. the use of a perioneometer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):10-16
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100004
To investigate the association of perinatal variables with the birth of very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm newborns.
It was a retrospective study of the medical records of infants born after spontaneous preterm labor with admission to a neonatal intensive care unit. Preterm infants were divided into two groups: very low birth weight (VLBW) group (weight <1,500 g) and low birth weight (LBW) group (weight ≥1,500 g and <2,500 g). Prenatal variables such as maternal complications during pregnancy and childbirth/postpartum, and fetal/neonatal complications were investigated. Statistical analysis was performed using the Fisher exact test or χ2 test, with calculation of relative risk (RR), and the Student t test for comparison of group means, with the level of significance set at p≤0.05.
Hemorrhagic comorbidities (p=0.006; RR=1.2) and hypertension (p=0.04; RR=1.5), surgical delivery (p=0.001; RR=0.5), gestational age <33 weeks (p< 0.001; RR=16.7) and Apgar score at 1st and 5th minute (p=0.006; RR=1.6; p=0.01; RR=1.9) were associated with the occurrence of VLBW. Infants with VLBW had a significant association with the occurrence of metabolic comorbidities (p=0.01; RR=1.8), neurological (p=0.01; RR=1.7) and infectious diseases (p=0.001; RR=1.9), hospitalization >4 weeks (p=0.02; RR=1.8) and early neonatal death (p=0.0001; RR=2.9).
Factors such as hypertension and bleeding comorbidities during delivery and management of gestational age of less than 33 weeks were associated with the birth of VLBW newborns. This group of infants also showed higher RR for the occurrence of early neonatal death.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):10-15
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005202
To determine if the presence of infectious agents in vaginal or cervical content can alter the results of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) test and the measurement of cervical length (CC) by transvaginal ultrasonography.
A total of 107 pregnant women with a history of spontaneous preterm birth were submitted to the phIGFBP-1 test and to measurement of CC by transvaginal ultrasonography every 3 weeks, between 24 and 34 weeks of gestation. Genital infections were determined immediately before testing. The patients were distributed into four groups (GA, GB, GC, and GD) and the correlation between genital infection and changes in the tests was determined within each group based on the odds ratio (OR) and the Pearson correlation coefficient.
In each group, over 50% of the patients had genital infections (GA 10/17; GB 28/42; GC 15/24; GD 35/53), with bacterial vaginosis being the main alteration of the vaginal flora. Positive results for phIGFBP-1(GA 10/10; GB 18/28; GC 15/15; GD 19/35) and CC≤20 mm (GA 10/10; GB 20/28; GC 10/15; GD 20/35) were obtained more frequently in patients with genital infection in all groups. Nonetheless, when applying the Pearson correlation coefficient we detected a poor correlation between genital infection and positivity for markers.
The presence of changes in the vaginal flora and of other genital infections does not significantly alter the results of phIGFBP-1 and the measurement of cervical length when compared to cases without infection. However, more studies with larger samples are necessary to confirm these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(1):10-16
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000100003
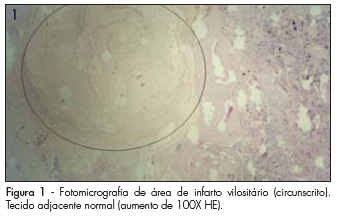
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of histopathological changes, in human placentas, related to hypertensive syndromes. METHODS: a transversal study that compares histopathological changes identified in 43 placentae from hypertensive pregnant women (HypPr), with the ones from 33 placentae from normotensive pregnant women (NorPr). The weight, volume and macroscopic and microscopic occurrence of infarctions, clots, hematomas, atherosis (partial obliteration, thickness of layers and presence of blood vessels hyalinization) and Tenney-Parker changes (absent, discreet and prominent), as well as the locating of infarctions and clots (central, peripheral or the association of both) have been analyzed. The χ2 and t Student tests have been used for the statistical analysis, as well as medians, standard deviations and ratios. It has been considered as significant, p<0.05. RESULTS: the macroscopic study of HypPr placentae have presented lower weight (461.1 versus 572.1 g) and volume (437.4 versus 542.0 cm³), higher infarction (51.2 versus 45.5%; p<0.05: OR=1.15) and clots (51.2 versus 15.1%; p<0.05; OR=5.4) ratios, as compared to the NorPr's. In the HypPr and NorPr, microscopic clots have occurred in 83.7 versus 45.5% (p<0.05; OR=4.3), respectively. Atherosis and Tenney-Parker changes have been statistically associated to the hypertensive syndromes (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the obtained data allow us to associate lower placentary weight and volume, higher ratio of macro and microscopic infarction, clots, atherosis and Tenney-Parker changes to placentae of gestations occurring with hypertensive syndromes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):100-108
In addition to being a medical phenomenon, pandemics affect the individual and society on several levels and lead to disruptions. In the pandemic process, different groups in the population, including pregnant women as a defenseless group, are subjected to psychological threat. The present study aimed to determine the levels of anxiety and depression and related factors in pregnant women during the the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic.
The present cross-sectional study was conducted with 269 pregnant women through face-to-face interviews held in Istanbul, Turkey. Regarding the data collection tools, the Cronbach α reliability coefficient was of 0.90 for the Beck Anxiety Inventory, and of 0.85 for the Beck Depression Inventory.
Among the participating pregnant women, 30.5% had mild, 17.5% had moderate, and 5.9% had severe anxiety symptoms, whereas 35.3% had mild, 16.7% had moderate, and 2.2% had severe depression symptoms. We found that those who were concerned about their health had 5.36 times (p=0.04) more risk of developing anxiety, and 4.82 times (p=0.01) more risk of developing depression than those who were not concerned. Those who had a history of psychiatric disease had 3.92 times (p=0.02) more risk of developing anxiety than those without it.
We determined that about half of the pregnant women included in the study had some degree of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. The risk factors for anxiety and depression among the pregnant women were determined as smoking, concerns about health and getting infectedwith the coronavirus, history of psychiatric disease, and undergoing regular antenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):100-100